2 Times Square Root Of 2
sandbardeewhy
Dec 01, 2025 · 10 min read
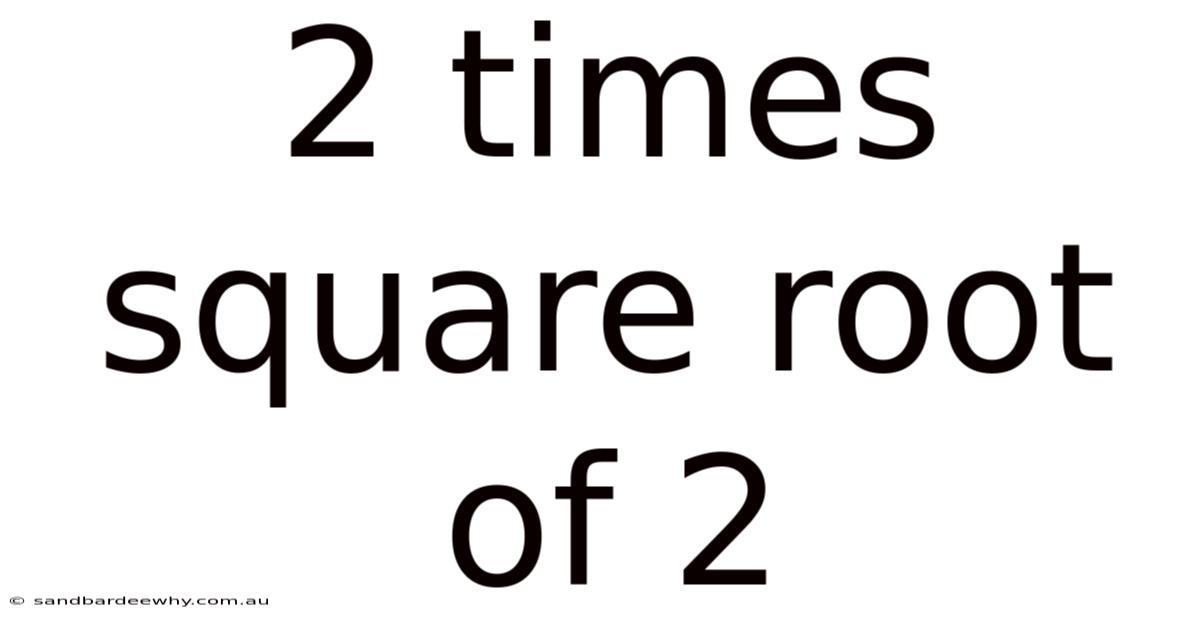
Table of Contents
Imagine you're meticulously arranging tiles to create a stunning mosaic. You've got squares, triangles, and circles, each contributing to the overall masterpiece. But then, you encounter a measurement that isn't a whole number, something beyond your standard ruler. This is where numbers like 2 times square root of 2 come into play, adding an element of mathematical elegance and precision to your design. These types of numbers aren't just abstract concepts; they're the hidden backbone of many real-world applications, from engineering to computer graphics.
Think about the screen you're reading this on. The clarity, resolution, and precise rendering of images rely on complex calculations, many of which involve irrational numbers like the square root of 2. Understanding 2 times square root of 2, therefore, opens a door to comprehending the intricate mathematical underpinnings of the world around us. It's about appreciating the beauty and utility of numbers that extend beyond the familiar integers, revealing a deeper layer of mathematical truth that governs much of our technological landscape. This article dives deep into the essence of this specific value, unraveling its mysteries and showcasing its significance in various fields.
Unveiling 2 Times Square Root of 2
The number 2 times square root of 2, often written as 2√2, holds a unique place in mathematics. At first glance, it may appear as just another irrational number, but its significance extends beyond a mere numerical value. It's a cornerstone in geometry, physics, and computer science, embodying a fundamental relationship between numbers and shapes. To fully appreciate its importance, we must first understand its context and the underlying principles that define it.
At its core, the square root of 2 (√2) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction a/b, where a and b are integers. This was a revolutionary discovery in ancient Greece, challenging the prevailing belief that all numbers could be expressed in such a way. Multiplying this irrational number by 2 gives us 2 times square root of 2, which is approximately 2.828427124746190097603377448419... and the digits continue infinitely without repeating. This number retains the irrationality of √2, but scales its magnitude, leading to its own unique applications and properties.
Comprehensive Overview
Definitions and Foundations
To understand 2 times square root of 2, we first need to break it down into its fundamental components: the square root and the concept of multiplication. The square root of a number x is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals x. In the case of √2, it represents a number that, when squared, gives 2. This number is irrational, meaning its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
When we multiply √2 by 2, we are essentially scaling the square root of 2 by a factor of 2. This can be visualized geometrically: if √2 represents the length of a line segment, then 2√2 represents a line segment twice as long. This simple multiplication transforms the magnitude of the number, but it doesn't alter its fundamental irrational nature.
Historical Significance
The discovery of the irrationality of √2 is a cornerstone of mathematical history. The ancient Greeks, particularly the Pythagoreans, initially believed that all numbers could be expressed as ratios of integers. However, the existence of √2 shattered this belief. Legend has it that Hippasus of Metapontum, a Pythagorean, was drowned at sea for revealing the existence of irrational numbers, as it contradicted the core tenets of their mathematical philosophy.
The number 2 times square root of 2, as a scaled version of √2, inherits this historical significance. It serves as a reminder of the limitations of early mathematical understanding and the subsequent expansion of mathematical thought to accommodate irrational numbers. Its presence in geometrical constructions and calculations underscores the importance of accepting and working with numbers beyond the realm of simple fractions.
Geometric Interpretation
The geometric interpretation of 2 times square root of 2 is particularly insightful. Consider a square with sides of length 2. The diagonal of this square can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem: a² + b² = c², where a and b are the sides of the square, and c is the length of the diagonal. In this case, 2² + 2² = c², which simplifies to 8 = c². Taking the square root of both sides, we find that c = √8. Since √8 = √(4*2) = 2√2, the diagonal of a square with sides of length 2 is precisely 2 times square root of 2.
This geometric representation provides a visual and intuitive understanding of the number. It connects an abstract numerical value to a concrete geometric shape, demonstrating its relevance in spatial measurements and constructions.
Mathematical Properties
2 times square root of 2 possesses several interesting mathematical properties. As an irrational number, it cannot be expressed as a terminating or repeating decimal. Its decimal representation extends infinitely without any discernible pattern. This makes it impossible to represent it exactly using a finite number of digits.
Furthermore, 2 times square root of 2 is an algebraic number, meaning it is a root of a polynomial equation with integer coefficients. Specifically, it is a root of the equation x² - 8 = 0. This property classifies it within the broader category of algebraic numbers, which includes all numbers that can be obtained as solutions to polynomial equations.
Applications in Science and Engineering
The number 2 times square root of 2 finds applications in various scientific and engineering contexts. In physics, it appears in calculations involving wave phenomena and quantum mechanics. Its precise value is crucial for modeling and predicting the behavior of physical systems.
In engineering, 2 times square root of 2 is used in structural analysis and design. It helps determine the stability and strength of structures by providing accurate measurements for diagonal supports and reinforcement. Its role in computer science includes graphics, image processing, and simulations, where it aids in rendering accurate and detailed visualizations.
Trends and Latest Developments
Recent trends in mathematics and technology continue to highlight the importance of irrational numbers like 2 times square root of 2. As computational power increases, so does the ability to perform complex calculations involving these numbers. This has led to new applications in fields such as cryptography, where irrational numbers are used to generate secure encryption keys.
Data from various research institutions indicate a growing interest in the use of irrational numbers in advanced algorithms and simulations. These numbers provide a level of precision and complexity that is essential for modeling real-world phenomena accurately. In popular opinion, there's also a growing appreciation for the beauty and elegance of these numbers, as they represent a deeper level of mathematical understanding.
Professional insights suggest that the future of many technologies will rely heavily on our ability to harness the properties of irrational numbers. As we continue to push the boundaries of scientific and technological innovation, 2 times square root of 2 and other similar numbers will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role.
Tips and Expert Advice
Practical Application in Design
When working with designs that require precision, understanding 2 times square root of 2 can be invaluable. For example, in architecture, if you're designing a square window with sides of 2 meters, the diagonal measurement (which would need reinforcement) is 2√2 meters. Knowing this allows for accurate planning and material allocation, ensuring the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of the design.
Moreover, in graphic design, when creating layouts or logos, the relationship between squares and their diagonals (involving 2 times square root of 2) can help maintain visual harmony and balance. Precise measurements ensure that elements are proportionally correct, resulting in a more pleasing and professional appearance.
Simplifying Calculations
While 2 times square root of 2 is an irrational number, there are ways to simplify calculations involving it. Instead of using the approximate decimal value (2.8284271247...), you can often work with the expression 2√2 directly in your equations. This maintains precision and avoids rounding errors that can accumulate over multiple calculations.
Additionally, remember that (2√2)² equals 8. This can be useful when simplifying more complex expressions or solving equations involving 2 times square root of 2. By recognizing these patterns and relationships, you can streamline your calculations and arrive at accurate results more efficiently.
Recognizing Patterns in Mathematics
Understanding 2 times square root of 2 also means recognizing its presence in various mathematical patterns. For example, it appears in trigonometric functions, particularly when dealing with angles related to 45-degree triangles. In these scenarios, knowing the exact value can simplify problem-solving.
Furthermore, 2 times square root of 2 can also be found in certain series and sequences. By identifying these occurrences, you can gain a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships and improve your problem-solving skills.
Using Technology Effectively
Technology can greatly assist in working with 2 times square root of 2. Scientific calculators can provide accurate approximations, and computer algebra systems (CAS) can perform symbolic calculations that retain the exact value.
Software such as Mathematica or Maple can handle complex expressions involving irrational numbers, allowing you to focus on the problem-solving process rather than the arithmetic. Utilizing these tools effectively can save time and reduce the risk of errors.
Incorporating into Computer Graphics
In computer graphics, 2 times square root of 2 is essential for scaling and rotating objects precisely. When creating 3D models or 2D animations, you often need to transform shapes and objects while maintaining their proportions. Understanding the relationship between squares and their diagonals ensures that your transformations are accurate and visually appealing.
Additionally, it aids in creating realistic lighting and shadow effects. Accurately calculating distances and angles (which often involve 2 times square root of 2) improves the realism of the rendering. This attention to detail can make a significant difference in the overall quality of the final product.
FAQ
Q: What is the exact value of 2 times square root of 2? A: 2 times square root of 2 is an irrational number, so it has an infinite, non-repeating decimal representation. Its approximate value is 2.828427124746190097603377448419..., but it cannot be expressed exactly as a finite decimal.
Q: Why is the square root of 2 irrational? A: The square root of 2 is irrational because it cannot be expressed as a fraction a/b, where a and b are integers. This can be proven mathematically using proof by contradiction.
Q: Where does 2 times square root of 2 appear in geometry? A: It appears as the length of the diagonal of a square with sides of length 2. This is derived from the Pythagorean theorem.
Q: Can I simplify expressions involving 2 times square root of 2? A: Yes, you can often simplify expressions by working with the expression 2√2 directly, rather than using a decimal approximation. Also, remember that (2√2)² equals 8, which can be helpful in simplifying more complex expressions.
Q: How is 2 times square root of 2 used in technology? A: It's used in computer graphics for precise scaling and rotations, in cryptography for generating secure encryption keys, and in advanced algorithms and simulations for modeling real-world phenomena accurately.
Conclusion
In summary, 2 times square root of 2 is more than just a number; it's a mathematical concept with deep historical roots, geometrical significance, and practical applications in various fields. Its irrational nature challenges our understanding of numbers and highlights the importance of precision in calculations and designs. From architecture to computer science, this seemingly simple number plays a crucial role in shaping our world.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of 2 times square root of 2, we encourage you to explore its applications further. Try using it in your own designs, calculations, or simulations. Share your findings and insights with others, and let's continue to unravel the mysteries and beauty of mathematics together. What creative ways can you apply this knowledge in your field of interest?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Effective Nuclear Charge
Dec 01, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 66 Cm
Dec 01, 2025
-
How Much Does 55 Gallons Of Water Weigh
Dec 01, 2025
-
Allusions In Romeo And Juliet Act 2 Scene 2
Dec 01, 2025
-
Oils And Waxes Are Examples Of
Dec 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 Times Square Root Of 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.