I Before E Except After C Exceptions
sandbardeewhy
Nov 30, 2025 · 11 min read
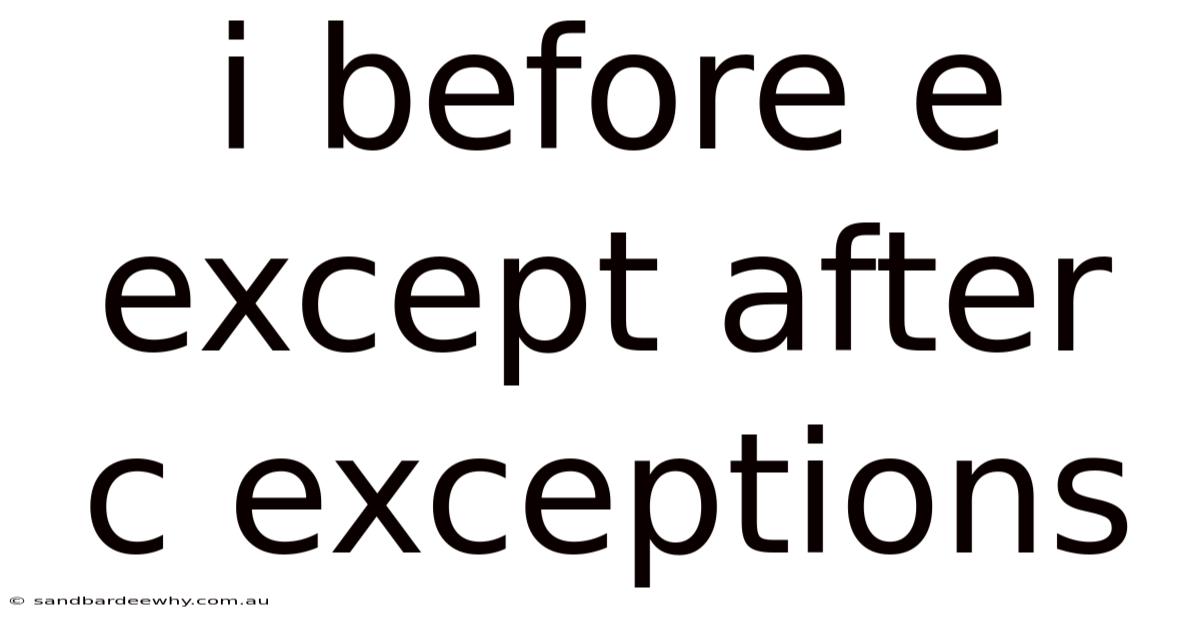
Table of Contents
Imagine you're a young student, bright-eyed and eager, confidently writing the word "believe" on a spelling test. You pause, a flicker of doubt crossing your face. Is it "ie" or "ei"? Your teacher’s voice echoes in your mind: "I before E, except after C." You smile, reassured, and continue. But then comes "receive," and the rule seems to falter. Confusion sets in. This simple yet perplexing guideline has tripped up countless students and adults alike, sparking debates and humorous anecdotes across generations.
The English language, with its rich history and diverse influences, is notorious for its quirks and inconsistencies. One of the most well-known, and often misleading, of these quirks is the "I before E, except after C" rule. While it holds true in many cases, the numerous exceptions can make it more of a hindrance than a help. Let's delve into the intricacies of this rule, exploring its origins, exceptions, and practical applications, to provide a comprehensive understanding that will clarify rather than confuse.
Main Subheading
The "I before E, except after C" rule is a mnemonic device intended to help learners remember the correct spelling of words containing the digraphs "ie" and "ei." A digraph is a combination of two letters that represent one sound. The rule suggests that when a word contains the "ee" sound, the letters should be arranged as "ie" (as in "believe"). However, when the "ee" sound follows the letter "c," the order should be reversed to "ei" (as in "receive").
This rule is deeply ingrained in English language education and is often one of the first spelling guidelines taught to children. Its simplicity and catchy nature make it memorable, which contributes to its widespread use. For many, it serves as a quick reference point when faced with spelling dilemmas. The problem is, the English language loves to break its own rules, and this one is no exception. Mastering English spelling requires a deeper understanding of the language's complexities and a more nuanced approach than simply relying on this single rule.
Comprehensive Overview
The "I before E, except after C" rule is rooted in the phonetics and historical development of the English language. Understanding its origins and the context in which it emerged can shed light on why it works in some cases and fails in others. The rule primarily applies to words where the "ie" or "ei" digraph produces a long "e" sound, as in "believe" or "receive."
The historical context is crucial. Many English words have origins in other languages, such as Latin, French, and German, each with its own spelling conventions. The "I before E" part of the rule can be traced back to the influence of Latin and French on English. In Latin, the "ie" combination often represented a distinct sound that was later adopted into English. The "except after C" clause reflects the way certain French-derived words were integrated into English orthography. In French, a "c" followed by an "e" often results in a soft "s" sound, and the "ei" combination was used to maintain this phonetic quality in words like "receive" and "deceive."
However, the English language is a melting pot of influences, and not all words followed these neatly defined patterns. Over time, inconsistencies arose due to various factors, including regional dialects, scribal errors, and the adoption of words from other languages that did not adhere to these conventions. This is why the rule, while helpful as a general guideline, is far from foolproof. The numerous exceptions can be categorized into several groups: words where the "ie" or "ei" does not make an "ee" sound, words with different etymological origins, and words that simply defy any logical explanation.
For instance, words like "height," "weigh," and "neighbor" contain the "ei" digraph, but the sound produced is not the long "e" sound. Similarly, words like "science" and "sufficient" do not follow the rule because the "ie" combination does not produce the "ee" sound. Furthermore, some words, like "weird" and "seize," have simply evolved over time to have spellings that contradict the rule.
Moreover, modern English has introduced new words and spellings that further complicate the application of the rule. The increasing use of abbreviations, acronyms, and informal language has led to the creation of words that do not conform to traditional spelling conventions. In summary, while the "I before E, except after C" rule provides a basic framework for understanding English spelling, its limitations are significant. A more comprehensive understanding of the language's etymology, phonetics, and historical development is necessary for mastering English spelling.
Trends and Latest Developments
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the limitations and potential confusion caused by the "I before E, except after C" rule. Many educators are now advocating for a more nuanced approach to teaching spelling, focusing on patterns, root words, and morphological awareness rather than relying solely on this mnemonic device.
One notable trend is the emphasis on teaching students about morphemes, the smallest units of meaning in a language. By understanding how words are constructed from root words, prefixes, and suffixes, students can develop a deeper understanding of spelling patterns and make more informed decisions about the correct spelling of unfamiliar words. For example, knowing that the root word "cede" means "to go" can help students remember the spelling of words like "recede" and "precede."
Another trend is the use of technology to enhance spelling instruction. Interactive spelling games, online dictionaries, and spell-checkers can provide students with immediate feedback and help them identify and correct their spelling errors. These tools can also be customized to focus on specific spelling patterns or problem areas, allowing for a more personalized and effective learning experience. Furthermore, corpus linguistics, the study of language based on large collections of real-world text, has provided valuable insights into the frequency and distribution of different spelling patterns. This data can be used to inform spelling instruction and prioritize the teaching of the most common and useful spelling rules and patterns.
The increasing awareness of the complexities of English spelling has also led to a more critical examination of the role of spelling rules in general. While some rules, like the "I before E, except after C" rule, are often unreliable, others can be quite helpful. For example, the rule that states that a final silent "e" is usually dropped before adding a suffix that begins with a vowel is generally consistent and useful. The key is to teach students to evaluate the reliability of different spelling rules and to use them judiciously, rather than blindly following them.
Professional insights suggest that effective spelling instruction should be integrated into a broader literacy curriculum that emphasizes reading, writing, and vocabulary development. Students who read widely and write frequently are more likely to develop a strong sense of spelling patterns and to internalize the correct spellings of common words. In addition, explicit instruction in phonics, the relationship between letters and sounds, can help students decode and spell unfamiliar words. By combining explicit instruction with rich literacy experiences, educators can help students become confident and competent spellers.
Tips and Expert Advice
Mastering English spelling can be a challenging but rewarding endeavor. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help you navigate the complexities of the "I before E, except after C" rule and improve your overall spelling skills:
-
Understand the Rule's Limitations: Recognize that the "I before E, except after C" rule is not a universal law. Be aware of its numerous exceptions and avoid relying on it blindly. Instead, use it as a starting point and be prepared to consult a dictionary or other resources when in doubt.
-
Focus on Root Words and Morphemes: Develop an understanding of root words, prefixes, and suffixes. This knowledge can help you break down complex words into smaller, more manageable parts and identify common spelling patterns. For example, if you know that the root word "cede" means "to go," you can use this knowledge to help you spell words like "precede" and "recede."
-
Learn Common Exceptions: Familiarize yourself with the most common exceptions to the "I before E, except after C" rule. These include words like "weird," "seize," "height," "neighbor," and "weigh." Creating a list of these exceptions and reviewing them regularly can help you commit them to memory.
-
Use Mnemonics and Memory Aids: Create your own mnemonics or memory aids to help you remember the correct spelling of difficult words. For example, you might remember that "weird" is spelled with "ei" by thinking of the phrase "Weird Edgar is interesting."
-
Read Widely and Write Frequently: Immerse yourself in the English language by reading a variety of texts, including books, articles, and newspapers. Pay attention to the spelling of words and try to notice common spelling patterns. In addition, practice writing regularly, whether it's journaling, writing emails, or composing essays. The more you read and write, the more you will internalize the correct spellings of words.
-
Use Technology Wisely: Take advantage of the technology available to you, such as online dictionaries, spell-checkers, and interactive spelling games. These tools can provide you with immediate feedback and help you identify and correct your spelling errors. However, be sure to use these tools as a supplement to your learning, rather than relying on them exclusively.
-
Practice Active Recall: Test yourself regularly on your spelling knowledge. Use flashcards, online quizzes, or simply ask a friend or family member to quiz you on a list of words. The act of actively recalling information from memory is a powerful way to reinforce learning and improve retention.
-
Seek Feedback and Learn from Mistakes: Don't be afraid to ask for feedback on your spelling. When someone points out a spelling error, take the time to understand why you made the mistake and how to correct it. Learning from your mistakes is an essential part of the learning process.
-
Be Patient and Persistent: Mastering English spelling takes time and effort. Don't get discouraged if you make mistakes or struggle with certain words. Be patient with yourself and keep practicing. With persistence and dedication, you can improve your spelling skills and become a more confident and competent writer.
By following these tips and expert advice, you can improve your spelling skills and navigate the complexities of the English language with greater confidence.
FAQ
Q: What is the "I before E, except after C" rule?
A: It's a mnemonic device to remember the spelling of words with "ie" or "ei," suggesting it's "ie" except after "c," where it becomes "ei."
Q: Is the "I before E, except after C" rule always correct?
A: No, it has many exceptions and should be used as a guideline, not a strict rule.
Q: Why does the rule have so many exceptions?
A: English words come from various languages, each with different spelling rules, causing inconsistencies.
Q: Can you give some examples of exceptions to the rule?
A: Words like "weird," "seize," "height," and "neighbor" don't follow the rule.
Q: How can I improve my spelling if the rule isn't reliable?
A: Focus on root words, learn common exceptions, read widely, write frequently, and use technology wisely.
Q: Are there any reliable spelling rules in English?
A: Yes, some rules, like dropping a silent "e" before adding a vowel suffix, are generally consistent.
Q: Should I teach the "I before E, except after C" rule to children?
A: It can be introduced as a starting point, but emphasize its limitations and teach alternative spelling strategies.
Q: What is the origin of this rule?
A: It originates from the influence of Latin and French on English, where specific letter combinations had distinct sounds.
Q: How does knowing root words help with spelling?
A: Understanding root words helps break down complex words, revealing spelling patterns.
Q: Is technology useful for improving spelling?
A: Yes, online dictionaries, spell-checkers, and interactive games can provide feedback and help correct errors.
Conclusion
The "I before E, except after C" rule, while a staple in English language education, is more of a guideline than a rigid rule. Its many exceptions can lead to confusion and frustration. By understanding the rule's origins, limitations, and common exceptions, learners can approach spelling with greater confidence and accuracy. Incorporating techniques like focusing on root words, reading widely, and utilizing technology can further enhance spelling skills.
Ultimately, mastering English spelling requires a multifaceted approach that combines knowledge of spelling rules with a deep understanding of the language's structure and history. Don't let the "I before E, except after C" rule be a stumbling block. Embrace the complexities of English spelling and continue to learn and explore the nuances of this fascinating language. Do you have any mnemonics or tricks that help you remember difficult spellings? Share them in the comments below and let's learn from each other!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write The Chemical Formula For Each Compound Described
Nov 30, 2025
-
120 Pounds Is How Many Kilograms
Nov 30, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In 69 Inches
Nov 30, 2025
-
What Is The Theme Of You Disappearing
Nov 30, 2025
-
How To Find Midpoint Of Two Points
Nov 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about I Before E Except After C Exceptions . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.