Is 2 5 Bigger Than 1 2
sandbardeewhy
Dec 03, 2025 · 10 min read
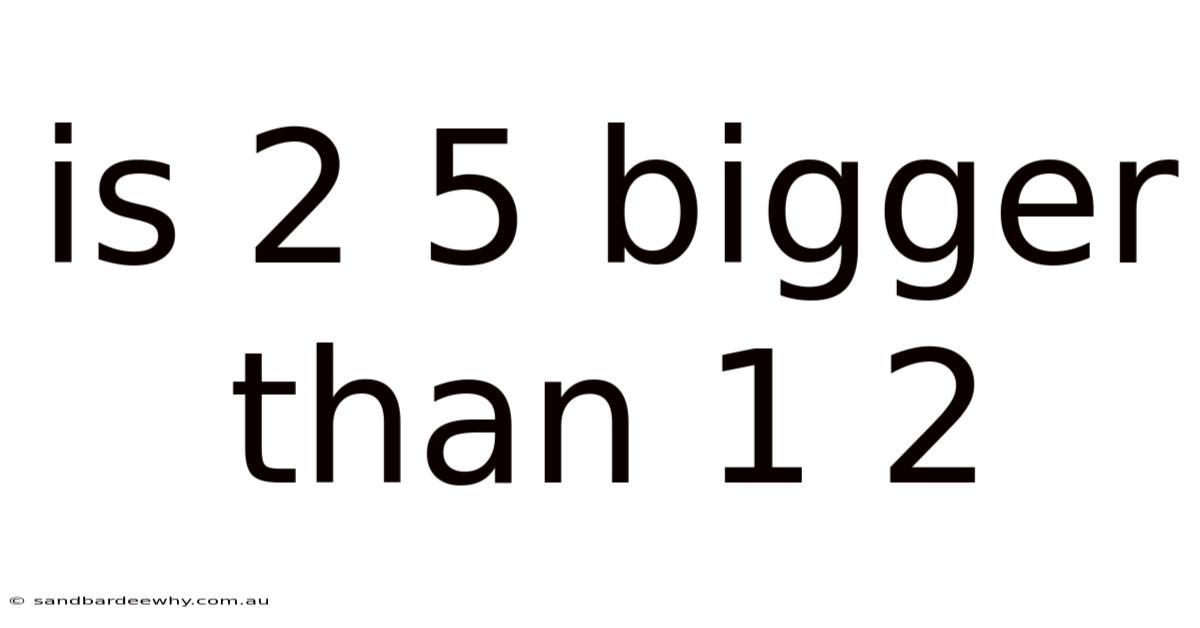
Table of Contents
The question "is 2/5 bigger than 1/2?" might seem simple, but it delves into fundamental concepts of fractions and comparisons. Fractions are an essential part of mathematics, encountered in everyday life from cooking to finances. A solid understanding of how to compare fractions is crucial for making informed decisions and solving more complex mathematical problems. This article will thoroughly explore the comparison between 2/5 and 1/2, covering various methods and providing a detailed explanation to ensure clarity.
Understanding Fractions
To accurately determine whether 2/5 is bigger than 1/2, it's important to understand what fractions represent. A fraction consists of two parts: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts of a whole you have, while the denominator indicates how many parts the whole is divided into. For example, in the fraction 2/5, the numerator 2 tells us that we have 2 parts, and the denominator 5 tells us that the whole is divided into 5 equal parts. Similarly, in the fraction 1/2, we have 1 part out of a whole that is divided into 2 equal parts.
Basic Concepts of Fractions
Before diving into the comparison of 2/5 and 1/2, let's review some basic concepts about fractions:
- Numerator: The number above the fraction bar, indicating the number of parts taken.
- Denominator: The number below the fraction bar, indicating the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
- Proper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator (e.g., 2/5).
- Improper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 5/2).
- Mixed Number: A number consisting of a whole number and a proper fraction (e.g., 2 1/2).
- Equivalent Fractions: Fractions that represent the same value, even though they have different numerators and denominators (e.g., 1/2 and 2/4).
Understanding these basic concepts is essential for comparing fractions and performing other operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Methods for Comparing Fractions
There are several methods to compare fractions, including:
- Common Denominator Method: Finding a common denominator for both fractions and comparing the numerators.
- Cross-Multiplication Method: Multiplying the numerator of one fraction by the denominator of the other and comparing the results.
- Decimal Conversion Method: Converting both fractions to decimals and comparing the decimal values.
- Visual Representation Method: Using diagrams or visual aids to represent the fractions and compare their sizes.
Each of these methods provides a different approach to comparing fractions, and the choice of method often depends on the specific fractions being compared and personal preference. We will explore each method in detail to compare 2/5 and 1/2.
Common Denominator Method
The common denominator method involves finding a common denominator for both fractions. A common denominator is a number that both denominators can divide into evenly. Once the fractions have a common denominator, you can compare their numerators directly. The fraction with the larger numerator is the larger fraction.
To compare 2/5 and 1/2 using the common denominator method:
- Find the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of the denominators: The denominators are 5 and 2. The LCM of 5 and 2 is 10.
- Convert each fraction to an equivalent fraction with the common denominator:
- For 2/5, multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 2: (2 * 2) / (5 * 2) = 4/10.
- For 1/2, multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 5: (1 * 5) / (2 * 5) = 5/10.
- Compare the numerators: Now we compare 4/10 and 5/10. The numerators are 4 and 5. Since 5 is greater than 4, 5/10 is greater than 4/10.
Therefore, 1/2 is greater than 2/5.
Cross-Multiplication Method
The cross-multiplication method is a quick way to compare two fractions. It involves multiplying the numerator of the first fraction by the denominator of the second fraction, and the numerator of the second fraction by the denominator of the first fraction. The fraction corresponding to the larger product is the larger fraction.
To compare 2/5 and 1/2 using the cross-multiplication method:
- Cross-multiply:
- Multiply the numerator of 2/5 (which is 2) by the denominator of 1/2 (which is 2): 2 * 2 = 4.
- Multiply the numerator of 1/2 (which is 1) by the denominator of 2/5 (which is 5): 1 * 5 = 5.
- Compare the products: We have 4 and 5. Since 5 is greater than 4, 1/2 is greater than 2/5.
This method provides a straightforward way to compare fractions without needing to find a common denominator.
Decimal Conversion Method
The decimal conversion method involves converting each fraction into its decimal equivalent and then comparing the decimal values. This method is particularly useful when dealing with fractions that are not easily converted to a common denominator.
To compare 2/5 and 1/2 using the decimal conversion method:
- Convert each fraction to a decimal:
- Divide 2 by 5: 2 ÷ 5 = 0.4.
- Divide 1 by 2: 1 ÷ 2 = 0.5.
- Compare the decimals: We have 0.4 and 0.5. Since 0.5 is greater than 0.4, 1/2 is greater than 2/5.
This method is intuitive and straightforward, especially when using a calculator.
Visual Representation Method
The visual representation method involves using diagrams or visual aids to represent the fractions and compare their sizes. This method is especially helpful for understanding the concept of fractions and can be particularly useful for visual learners.
To compare 2/5 and 1/2 using the visual representation method:
- Draw two identical rectangles:
- Divide the first rectangle into 5 equal parts and shade 2 of those parts to represent 2/5.
- Divide the second rectangle into 2 equal parts and shade 1 of those parts to represent 1/2.
- Compare the shaded areas: By visually comparing the shaded areas of the two rectangles, it is clear that the shaded area representing 1/2 is larger than the shaded area representing 2/5.
Therefore, 1/2 is greater than 2/5. This method provides a clear visual representation of the fractions, making it easier to understand the comparison.
Trends and Latest Developments
In recent years, there has been a renewed focus on improving mathematics education, particularly in the area of fractions. Research indicates that a strong foundation in fractions is crucial for success in algebra and higher-level mathematics. Educational platforms and apps are increasingly incorporating interactive tools and visual aids to help students understand and compare fractions more effectively.
Educational Technology
Educational technology has played a significant role in enhancing the understanding of fractions. Interactive tools such as virtual manipulatives, fraction bars, and dynamic software allow students to explore fractions in a hands-on and engaging way. These tools provide immediate feedback and allow students to visualize the concepts of fractions, making them more accessible and understandable.
Research on Fraction Understanding
Recent research in mathematics education emphasizes the importance of conceptual understanding of fractions. Traditional methods often focus on rote memorization of rules and procedures, which can lead to superficial understanding. Current approaches advocate for a deeper, more intuitive understanding of fractions through the use of visual models, real-world examples, and problem-solving activities.
Common Misconceptions
Despite the importance of fractions, many students struggle with understanding them. Common misconceptions include:
- Thinking that the larger the denominator, the larger the fraction (e.g., believing that 1/5 is greater than 1/2).
- Adding or subtracting fractions without finding a common denominator.
- Not understanding the concept of equivalent fractions.
Addressing these misconceptions through targeted instruction and practice is essential for building a solid foundation in fractions.
Tips and Expert Advice
To improve your understanding and skills in comparing fractions, consider the following tips and expert advice:
Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is key to mastering fractions. Work through a variety of problems involving different types of fractions and different comparison methods. Use online resources, textbooks, and worksheets to practice regularly.
Use Visual Aids
Visual aids such as fraction bars, number lines, and diagrams can be extremely helpful in understanding and comparing fractions. Draw diagrams to represent fractions and compare their sizes visually.
Understand the Concept of Equivalence
Make sure you understand the concept of equivalent fractions. Knowing how to find equivalent fractions is essential for comparing fractions using the common denominator method.
Relate Fractions to Real-World Examples
Relate fractions to real-world examples to make them more meaningful and understandable. For example, think about sharing a pizza or measuring ingredients in a recipe.
Seek Help When Needed
Don't hesitate to seek help from teachers, tutors, or online resources if you are struggling with fractions. Getting timely assistance can prevent misconceptions from becoming ingrained.
Understand the "Why" Not Just the "How"
Focus on understanding the underlying concepts of fractions, rather than just memorizing rules and procedures. Understanding why a particular method works will help you remember it and apply it correctly in different situations.
Start with the Basics
Ensure you have a solid understanding of basic fraction concepts such as numerators, denominators, proper fractions, and improper fractions before moving on to more complex topics.
Break Down Complex Problems
Break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps. This can make the problem seem less daunting and easier to solve.
Check Your Work
Always check your work to ensure that you have not made any mistakes. Use a different method to compare the fractions and verify that you get the same result.
FAQ
Q: What is a fraction?
A: A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of a numerator (the top number) and a denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts of the whole you have, and the denominator indicates how many parts the whole is divided into.
Q: How do you find a common denominator?
A: To find a common denominator, you need to find a number that both denominators can divide into evenly. The least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators is often used as the common denominator.
Q: What is cross-multiplication?
A: Cross-multiplication is a method for comparing two fractions. It involves multiplying the numerator of the first fraction by the denominator of the second fraction, and the numerator of the second fraction by the denominator of the first fraction. The fraction corresponding to the larger product is the larger fraction.
Q: How do you convert a fraction to a decimal?
A: To convert a fraction to a decimal, divide the numerator by the denominator. For example, to convert 1/2 to a decimal, divide 1 by 2, which equals 0.5.
Q: Why is it important to understand fractions?
A: Understanding fractions is essential for success in mathematics and everyday life. Fractions are used in various contexts, including cooking, finance, engineering, and science.
Q: What are equivalent fractions?
A: Equivalent fractions are fractions that represent the same value, even though they have different numerators and denominators. For example, 1/2 and 2/4 are equivalent fractions.
Q: How can visual aids help in understanding fractions?
A: Visual aids such as fraction bars, number lines, and diagrams can provide a concrete representation of fractions, making it easier to understand their relative sizes and values.
Conclusion
In summary, when comparing the fractions 2/5 and 1/2, we find that 1/2 is bigger than 2/5. This can be demonstrated through various methods, including finding a common denominator, cross-multiplication, decimal conversion, and visual representation. A solid understanding of fractions is crucial for mathematical proficiency and everyday applications. By using the methods and tips discussed in this article, you can confidently compare fractions and enhance your mathematical skills.
We encourage you to practice comparing fractions using different methods to solidify your understanding. Share this article with others who may benefit from it, and leave a comment below with any questions or insights you have about comparing fractions. Happy calculating!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
12 Gallons Equals How Many Quarts
Dec 03, 2025
-
Lyrics Of Ave Maria Song In English
Dec 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Limitation Of The Autoclave
Dec 03, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Molecules Contains The Fewest Covalent Bonds
Dec 03, 2025
-
What Are The Characteristics Of Culture
Dec 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 2 5 Bigger Than 1 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.