What 17 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit
sandbardeewhy
Nov 30, 2025 · 11 min read
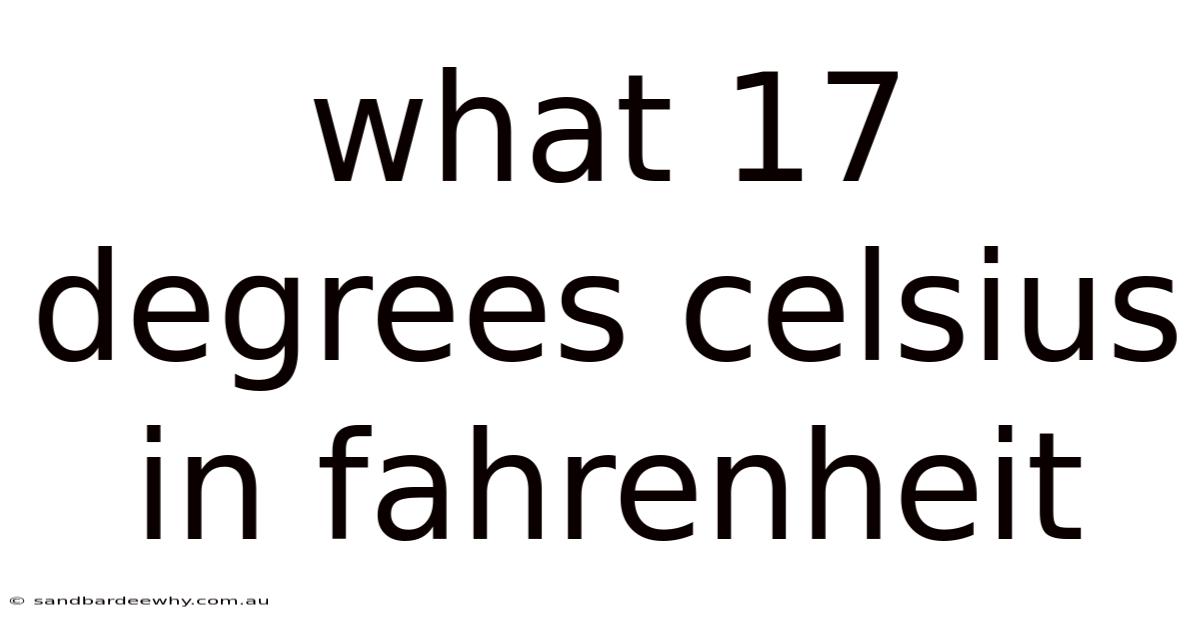
Table of Contents
The weather forecast announces a crisp 17 degrees Celsius. You pause, wondering what that feels like in Fahrenheit. Is it warm enough for a light jacket, or do you need to bundle up? Converting temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a common task, especially when traveling or following international weather reports.
Understanding temperature conversions is more than just a practical skill; it’s about connecting with different cultures and systems of measurement. While much of the world relies on Celsius, the United States still predominantly uses Fahrenheit. This difference can lead to confusion, but with a simple conversion, you can easily translate 17 degrees Celsius into its Fahrenheit equivalent and know exactly what to expect.
Understanding Temperature Scales: Celsius and Fahrenheit
Temperature scales are fundamental tools for measuring and understanding the thermal conditions around us. Celsius and Fahrenheit are two of the most widely used scales, each with its own history, design, and application. Grasping the basics of these scales is essential for accurate temperature interpretation and conversion.
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is part of the metric system and is used by most countries worldwide. It was developed by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in the 18th century. The Celsius scale is defined by two fixed points: the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point of water at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. The range between these points is divided into 100 equal parts, hence the name "centigrade" (centi- meaning hundred, and -grade meaning steps or degrees). This straightforward and logical structure makes Celsius easy to understand and use for scientific and everyday purposes.
The Fahrenheit scale, on the other hand, is primarily used in the United States, its territories, and a few other countries. It was created by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century. Fahrenheit based his scale on a mixture of brine (salt and water), setting 0°F as the freezing point of the brine. He then defined 32°F as the freezing point of pure water and 212°F as the boiling point of pure water. One notable characteristic of the Fahrenheit scale is that a one-degree Fahrenheit change is smaller than a one-degree Celsius change, making it seem more precise for measuring air temperature. However, this also means the Fahrenheit scale has a more complex relationship to physical phenomena compared to Celsius.
The Conversion Formula: Celsius to Fahrenheit
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, you can use a straightforward formula. This formula accurately translates temperatures from one scale to the other, ensuring you can understand temperature readings regardless of the system used. Here’s the formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let’s break down this formula:
- °C represents the temperature in Celsius.
- 9/5 is the conversion factor that accounts for the different sizes of the degree increments between the two scales.
- 32 is the offset added to adjust for the different zero points of the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales.
To convert 17 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, you would plug 17 into the formula:
°F = (17 × 9/5) + 32 °F = (17 × 1.8) + 32 °F = 30.6 + 32 °F = 62.6
Therefore, 17 degrees Celsius is equal to 62.6 degrees Fahrenheit.
Step-by-Step Calculation: Converting 17°C to Fahrenheit
Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit involves a simple calculation that can be easily done with or without a calculator. Here’s a step-by-step guide to converting 17°C to Fahrenheit:
-
Multiply by 9/5 (or 1.8): The first step is to multiply the Celsius temperature by the conversion factor 9/5, which is equivalent to 1.8. This adjusts for the difference in the size of the degree increments between the two scales. 17 °C × 1.8 = 30.6
-
Add 32: The next step is to add 32 to the result. This accounts for the difference in the zero points of the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. 30. 6 + 32 = 62.6
So, 17 degrees Celsius is equal to 62.6 degrees Fahrenheit.
Why the Conversion Matters: Practical Applications
Understanding how to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit has numerous practical applications in various aspects of daily life and specific fields. Whether you’re traveling, cooking, or working in a scientific environment, the ability to convert temperatures accurately is invaluable.
For travelers, temperature conversion is essential for understanding weather forecasts and adjusting to local conditions. If you're used to Celsius and are visiting a country that uses Fahrenheit, knowing how to convert temperatures will help you pack appropriately and plan your activities. For instance, if a weather forecast in the United States predicts a temperature of 70°F, converting it to Celsius (approximately 21°C) will give you a clearer sense of whether you need a light jacket or if it’s warm enough for short sleeves.
In the culinary world, accurate temperature conversions are crucial for cooking and baking. Many recipes, especially those from international sources, provide temperatures in Celsius. Converting these temperatures to Fahrenheit ensures that you set your oven or stovetop to the correct heat, which is essential for achieving the desired results. For example, if a French recipe calls for baking a cake at 180°C, knowing that this is approximately 356°F will help you bake the cake perfectly.
In scientific and technical fields, precise temperature measurements are vital for experiments, research, and manufacturing processes. While Celsius is commonly used in scientific contexts, there may be situations where Fahrenheit is required, particularly in older equipment or when collaborating with colleagues who use the Fahrenheit scale. Accurate conversions ensure consistency and reliability in data collection and analysis.
Historical Context: The Origins of Celsius and Fahrenheit
The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales have rich historical backgrounds, each developed by scientists with unique approaches to measuring temperature. Understanding their origins provides insight into why these scales are still in use today and how they have influenced our understanding of temperature.
Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, created the Celsius scale in 1742. Initially, Celsius designed his scale with 0 degrees as the boiling point of water and 100 degrees as the freezing point. However, after his death, the scale was inverted to its current form, with 0°C representing the freezing point and 100°C representing the boiling point of water. Celsius chose these reference points because of their significance in everyday life and scientific experiments. The simplicity and logical structure of the Celsius scale made it easy to adopt and use, leading to its widespread acceptance in the scientific community and most of the world.
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, developed the Fahrenheit scale in the early 18th century. Fahrenheit based his scale on several reference points. He initially set 0°F as the freezing point of a brine solution (a mixture of water, ice, and ammonium chloride salt), which was the lowest temperature he could reliably reproduce in his laboratory. He then defined 32°F as the freezing point of pure water and 212°F as the boiling point of pure water. One of the reasons Fahrenheit chose these specific points was to avoid negative numbers for typical ambient temperatures. Although the Fahrenheit scale is less intuitive than the Celsius scale, it became widely used in English-speaking countries, particularly in the British Empire and later in the United States.
Trends and Popular Opinions: Celsius vs. Fahrenheit
The debate over whether to use Celsius or Fahrenheit continues to this day, with strong opinions on both sides. While Celsius is the standard in most of the world due to its simplicity and scientific basis, Fahrenheit maintains a significant presence, particularly in the United States. Understanding the trends and popular opinions surrounding these scales can provide a broader perspective on temperature measurement.
Globally, the trend is overwhelmingly in favor of Celsius. Most countries use Celsius for weather forecasts, scientific research, and everyday measurements. The metric system, of which Celsius is a part, is the standard system of measurement in science and is widely adopted in international trade and commerce. This global standardization makes communication and collaboration easier across borders.
In the United States, however, Fahrenheit remains the dominant scale for everyday use. Many Americans grew up with Fahrenheit and are more comfortable using it for understanding weather conditions and cooking temperatures. There is also a cultural aspect to the preference for Fahrenheit; some view it as a part of American identity and resist the adoption of the metric system, including Celsius.
Despite the widespread use of Fahrenheit in the U.S., there are increasing calls for a transition to Celsius. Proponents of Celsius argue that it would align the U.S. with the rest of the world, simplify international interactions, and improve scientific accuracy. They point to the fact that many industries in the U.S., such as science, technology, and medicine, already use Celsius.
Tips and Expert Advice: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Mastering temperature conversions between Celsius and Fahrenheit can be incredibly useful in a variety of situations. Here are some tips and expert advice to help you become proficient in converting temperatures:
-
Use Online Conversion Tools: Numerous online tools and mobile apps can quickly and accurately convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit. These tools are particularly helpful when you need a precise conversion without doing the math manually. Simply enter the temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit, and the tool will instantly provide the equivalent temperature in the other scale. Some popular online converters include Google's built-in converter, as well as dedicated temperature conversion websites and apps.
-
Memorize Key Temperatures: Memorizing a few key temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit can provide a useful reference point for estimating conversions. For example, knowing that 0°C is 32°F (freezing point of water), 10°C is 50°F (cool weather), 20°C is 68°F (room temperature), 30°C is 86°F (warm weather), and 100°C is 212°F (boiling point of water) can help you quickly gauge approximate temperatures.
-
Practice Mental Conversions: With a little practice, you can learn to perform approximate temperature conversions in your head. A useful technique is to first multiply the Celsius temperature by 2 (instead of 1.8) and then add 30 (instead of 32). While this method is not perfectly accurate, it provides a reasonable estimate for everyday use. For example, to convert 25°C to Fahrenheit mentally, you would multiply 25 by 2 to get 50, and then add 30 to get 80°F, which is close to the actual value of 77°F.
-
Understand the Context: Consider the context in which you are using the temperature. For example, when checking the weather forecast, a rough estimate might be sufficient. However, when cooking or conducting a scientific experiment, precision is crucial. In these cases, always use a precise conversion method or tool.
-
Use Conversion Charts: Keep a conversion chart handy, especially in situations where you frequently need to convert temperatures. You can find and print conversion charts online or create your own. These charts typically list common temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, making it easy to quickly find the equivalent value.
FAQ: Common Questions About Temperature Conversion
Q: What is the formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit? A: The formula to convert Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F) is: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32.
Q: Why is 32 added in the Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion? A: The addition of 32 accounts for the difference in the zero points between the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. The freezing point of water is 0°C and 32°F, so 32 is added to align the scales.
Q: Is there a quick way to estimate Celsius to Fahrenheit? A: Yes, a quick estimation method is to multiply the Celsius temperature by 2 and add 30. While not perfectly accurate, this provides a reasonable approximation for everyday use.
Q: Why do some countries use Fahrenheit instead of Celsius? A: The use of Fahrenheit in some countries, particularly the United States, is largely due to historical reasons and cultural preference. The Fahrenheit scale was widely adopted in English-speaking countries before the metric system became the international standard.
Q: How accurate are online temperature converters? A: Online temperature converters are generally very accurate, as they use the precise conversion formula. However, it's always a good idea to double-check the result if accuracy is critical.
Q: Can I convert negative Celsius temperatures to Fahrenheit? A: Yes, the same formula applies to negative Celsius temperatures. For example, to convert -10°C to Fahrenheit: °F = (-10 × 9/5) + 32 °F = (-10 × 1.8) + 32 °F = -18 + 32 °F = 14 So, -10°C is equal to 14°F.
Conclusion
Converting 17 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit involves a simple calculation that yields 62.6°F. This conversion is not just a mathematical exercise; it's a practical skill that bridges understanding across different measurement systems. Whether you're planning a trip, following international news, or just curious, knowing how to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit enhances your ability to interpret and adapt to various temperature readings.
Now that you understand the conversion process, why not try converting other temperatures? Practice with different values to become more comfortable with the process, or use an online tool to explore various conversions. Share your findings with friends and family, and help them understand the differences between Celsius and Fahrenheit. By mastering this skill, you'll be better equipped to navigate a world that uses multiple temperature scales.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats A Group Of Chickens Called
Nov 30, 2025
-
Valley Of Ashes In Great Gatsby
Nov 30, 2025
-
When In God We Trust Added To Money
Nov 30, 2025
-
What Are 3 Products Of Cellular Respiration
Nov 30, 2025
-
How Many Nanograms In A Mg
Nov 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What 17 Degrees Celsius In Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.