What Amount Is 10 More Than 90
sandbardeewhy
Dec 04, 2025 · 11 min read
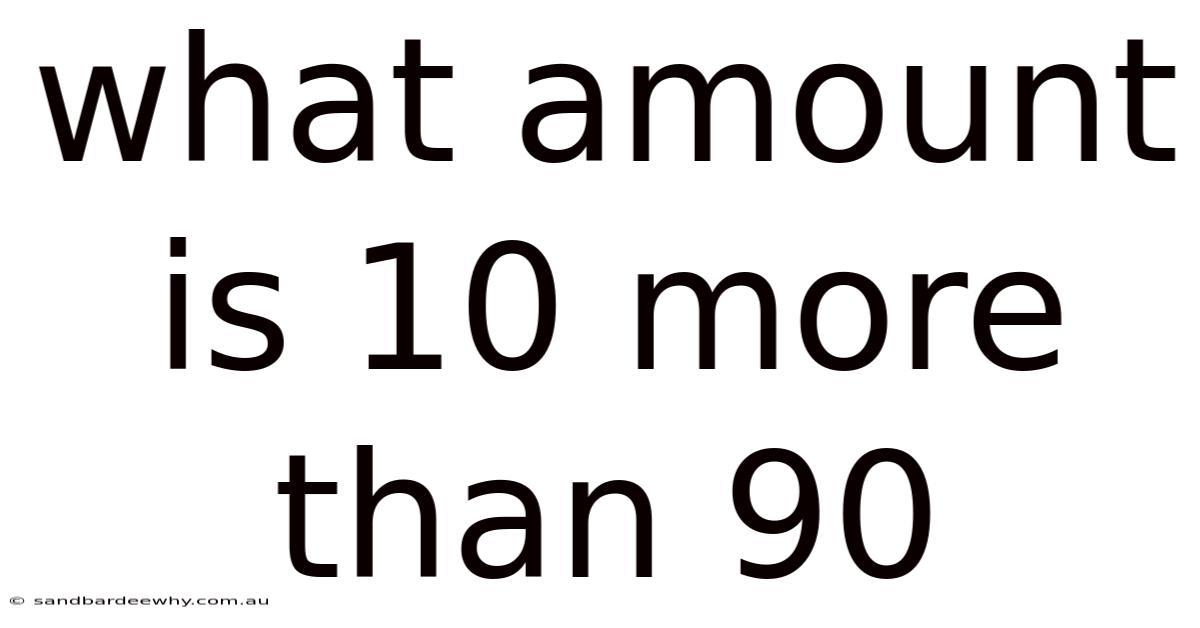
Table of Contents
Have you ever paused to consider the simplicity behind seemingly straightforward math problems? We often rush through basic arithmetic, yet within it lies a foundation for more complex understanding. Imagine a child learning to count, their face lighting up as they grasp that adding just a little bit more can change everything.
The question "What amount is 10 more than 90?" might seem elementary, but it's a perfect example of how fundamental math concepts build our analytical skills. It’s not just about finding the right number; it’s about understanding addition and numerical relationships. Let’s delve into this topic, exploring its essence, its applications, and why such simple questions still hold value.
Understanding the Basics: What is 10 More Than 90?
At its core, the question "What amount is 10 more than 90?" is an exercise in basic addition. It requires understanding the operation of adding one number to another to find their sum. This type of problem is foundational to arithmetic and serves as a building block for more complex mathematical concepts. The answer, of course, is 100. But let's break down why this seemingly simple question is more significant than it appears.
The Foundation of Arithmetic
Arithmetic is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It deals with numbers and the basic operations that can be performed on them, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Addition, in particular, is a fundamental concept that starts with understanding how to combine quantities. Asking "What amount is 10 more than 90?" is a direct application of this principle, reinforcing the idea that addition combines two or more numbers to find their total value.
Place Value and Number Sense
Understanding place value is crucial in solving this problem efficiently. The number 90 consists of 9 tens and 0 ones. Adding 10 to it means increasing the tens by one, resulting in 10 tens, which is 100. This simple calculation reinforces the concept of place value, which is essential for performing more complex arithmetic operations. Number sense, the intuitive understanding of numbers and their relationships, also comes into play here. Recognizing that 10 is a significant increment relative to 90 allows for a quick mental calculation.
A Comprehensive Overview of Addition and Numerical Relationships
To appreciate the simplicity of finding what amount is 10 more than 90, it's helpful to explore the broader context of addition and numerical relationships. These concepts are not only fundamental to mathematics but also have practical applications in everyday life.
The Concept of Addition
Addition is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, along with subtraction, multiplication, and division. It involves combining two or more numbers, known as addends, to find their total, known as the sum. In the case of "What amount is 10 more than 90?", 90 and 10 are the addends, and the sum is 100.
Addition is both commutative and associative. The commutative property states that the order of the addends does not affect the sum (a + b = b + a). For example, 10 + 90 is the same as 90 + 10. The associative property states that the way addends are grouped does not affect the sum (a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c). These properties make addition flexible and easier to perform in various contexts.
Historical Roots of Addition
The concept of addition dates back to ancient civilizations. Early forms of counting and arithmetic were used in trade, agriculture, and construction. The Egyptians, for example, used a base-10 number system and developed methods for addition and subtraction. The Babylonians also had a sophisticated number system and made significant contributions to arithmetic.
The modern symbols for addition (+) and subtraction (−) emerged during the Renaissance. Before these symbols were widely adopted, mathematicians used words or abbreviations to indicate addition and subtraction. The standardization of these symbols helped to streamline mathematical notation and made it easier to communicate mathematical ideas.
Numerical Relationships
Understanding numerical relationships involves recognizing how numbers relate to each other in terms of magnitude, order, and patterns. In the problem "What amount is 10 more than 90?", the relationship between 10 and 90 is crucial. Recognizing that 10 is a tenth of 100 and that adding it to 90 completes the hundred is an example of understanding numerical relationships.
Number lines are a useful tool for visualizing numerical relationships. A number line is a straight line on which numbers are placed at intervals, showing their relative positions. On a number line, adding 10 to 90 can be represented by moving 10 units to the right from 90, landing on 100. This visual representation helps to reinforce the concept of addition and numerical relationships.
Practical Applications of Addition
Addition is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life. From calculating expenses to measuring ingredients in a recipe, addition is an essential skill. In finance, addition is used to calculate total income, expenses, and profits. In construction, it is used to measure lengths, areas, and volumes. In cooking, it is used to combine ingredients in the correct proportions.
Understanding addition also helps in developing problem-solving skills. Real-world problems often require breaking them down into smaller steps, each involving addition. For example, calculating the total cost of items in a shopping cart involves adding the prices of each item.
The Role of Mental Math
Mental math involves performing calculations in one's head without the aid of calculators or other tools. Practicing mental math can improve number sense, enhance problem-solving skills, and boost confidence in one's mathematical abilities. The question "What amount is 10 more than 90?" is an excellent example of a problem that can be easily solved using mental math.
Strategies for mental math include breaking down numbers into smaller parts, using number patterns, and visualizing numbers. For example, to add 10 to 90 mentally, one can think of 90 as 9 tens and then add one more ten to get 10 tens, which is 100.
Trends and Latest Developments in Math Education
Math education is constantly evolving, with new trends and developments aimed at improving students' understanding and proficiency in mathematics. Understanding these trends can provide insights into how basic concepts like addition are taught and reinforced.
Emphasis on Conceptual Understanding
One of the major trends in math education is the emphasis on conceptual understanding rather than rote memorization. Traditional math education often focused on memorizing formulas and procedures without necessarily understanding the underlying concepts. Modern approaches prioritize understanding why mathematical concepts work, allowing students to apply them more flexibly and creatively.
For example, instead of just memorizing the addition algorithm, students are encouraged to understand the concept of combining quantities and the role of place value. This deeper understanding helps them to solve problems in different contexts and to develop a stronger foundation for more advanced mathematics.
Use of Technology in Math Education
Technology plays an increasingly important role in math education. Interactive software, educational apps, and online resources can provide students with engaging and personalized learning experiences. Technology can also help to visualize abstract concepts and to provide immediate feedback on students' work.
For example, virtual manipulatives can be used to represent numbers and to demonstrate addition and subtraction operations. Online games and quizzes can provide students with opportunities to practice their skills in a fun and interactive way.
Focus on Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
Modern math education places a strong emphasis on problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Students are encouraged to apply their mathematical knowledge to solve real-world problems and to develop their analytical skills. This approach helps to make math more relevant and engaging for students.
For example, instead of just solving routine addition problems, students might be asked to solve word problems that require them to use addition in a practical context. This helps them to see the value of math in everyday life and to develop their problem-solving skills.
Integration of Math with Other Subjects
Another trend in math education is the integration of math with other subjects, such as science, technology, engineering, and art (STEM). This interdisciplinary approach helps students to see the connections between different subjects and to apply their mathematical knowledge in a broader context.
For example, students might use math to analyze data in a science experiment, to design a structure in an engineering project, or to create a piece of art using geometric principles. This integration helps to make math more relevant and engaging for students and to develop their critical thinking skills.
Tips and Expert Advice for Mastering Basic Arithmetic
Mastering basic arithmetic, including addition, is essential for success in mathematics and in many areas of life. Here are some tips and expert advice for improving your arithmetic skills:
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, arithmetic requires regular practice to master. Set aside some time each day to practice addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Use worksheets, online resources, or mental math exercises to reinforce your skills. Regular practice will help to build your confidence and to improve your speed and accuracy.
For example, start with simple addition problems and gradually increase the difficulty. Use flashcards to memorize basic addition facts. Practice mental math while doing everyday tasks, such as calculating the total cost of items in a shopping cart.
Understand the Underlying Concepts
Focus on understanding the underlying concepts of arithmetic, rather than just memorizing procedures. Understand why addition works and how it relates to other mathematical operations. This deeper understanding will help you to solve problems more flexibly and creatively.
For example, learn about the commutative and associative properties of addition. Understand the concept of place value and how it relates to addition and subtraction. Use visual aids, such as number lines and manipulatives, to reinforce your understanding.
Use Visual Aids and Manipulatives
Visual aids and manipulatives can be very helpful for understanding arithmetic concepts. Number lines, base-10 blocks, and other visual tools can help to make abstract concepts more concrete and to provide a visual representation of mathematical operations.
For example, use a number line to visualize addition and subtraction. Use base-10 blocks to represent numbers and to demonstrate addition and subtraction operations. Use diagrams and charts to organize information and to solve problems.
Break Down Problems into Smaller Steps
When faced with a complex arithmetic problem, break it down into smaller, more manageable steps. This will make the problem less intimidating and will help you to solve it more accurately.
For example, when adding large numbers, start by adding the ones digits, then the tens digits, then the hundreds digits, and so on. Carry over any extra digits to the next column. Check your work by estimating the answer and comparing it to your calculated answer.
Use Real-World Examples
Connect arithmetic concepts to real-world examples to make them more relevant and engaging. This will help you to see the value of arithmetic in everyday life and to develop your problem-solving skills.
For example, calculate the total cost of items in a shopping cart. Measure ingredients in a recipe and adjust the quantities as needed. Calculate the distance and time required for a trip.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Basic Arithmetic
Here are some frequently asked questions about basic arithmetic:
Q: What is the difference between addition and subtraction? A: Addition combines two or more numbers to find their total, while subtraction finds the difference between two numbers.
Q: What are the properties of addition? A: Addition is commutative (a + b = b + a) and associative (a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c).
Q: How can I improve my mental math skills? A: Practice regularly, use number patterns, and break down problems into smaller steps.
Q: What are some real-world applications of arithmetic? A: Calculating expenses, measuring ingredients, and budgeting finances.
Q: Why is understanding place value important in arithmetic? A: Place value helps in performing arithmetic operations accurately and efficiently by understanding the value of each digit in a number.
Conclusion
So, what amount is 10 more than 90? The answer, 100, might seem simple, but it's a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. By grasping fundamental concepts like addition, place value, and numerical relationships, we build a solid foundation for tackling more complex problems. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply someone looking to sharpen your skills, mastering basic arithmetic is an invaluable asset.
Ready to put your math skills to the test? Try solving similar problems and explore other areas of arithmetic. Share your solutions and insights in the comments below, and let's continue this journey of learning together!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Big Is The Mona Lisa Portrait
Dec 04, 2025
-
How Do You Calculate The Rate Of Natural Increase
Dec 04, 2025
-
6 Foot 1 Inches In Cm
Dec 04, 2025
-
According To Chomskys Theory Of Language Acquisition
Dec 04, 2025
-
List Two Signs That A Chemical Reaction Has Taken Place
Dec 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Amount Is 10 More Than 90 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.