What Is 3 To The 0 Power
sandbardeewhy
Nov 30, 2025 · 10 min read
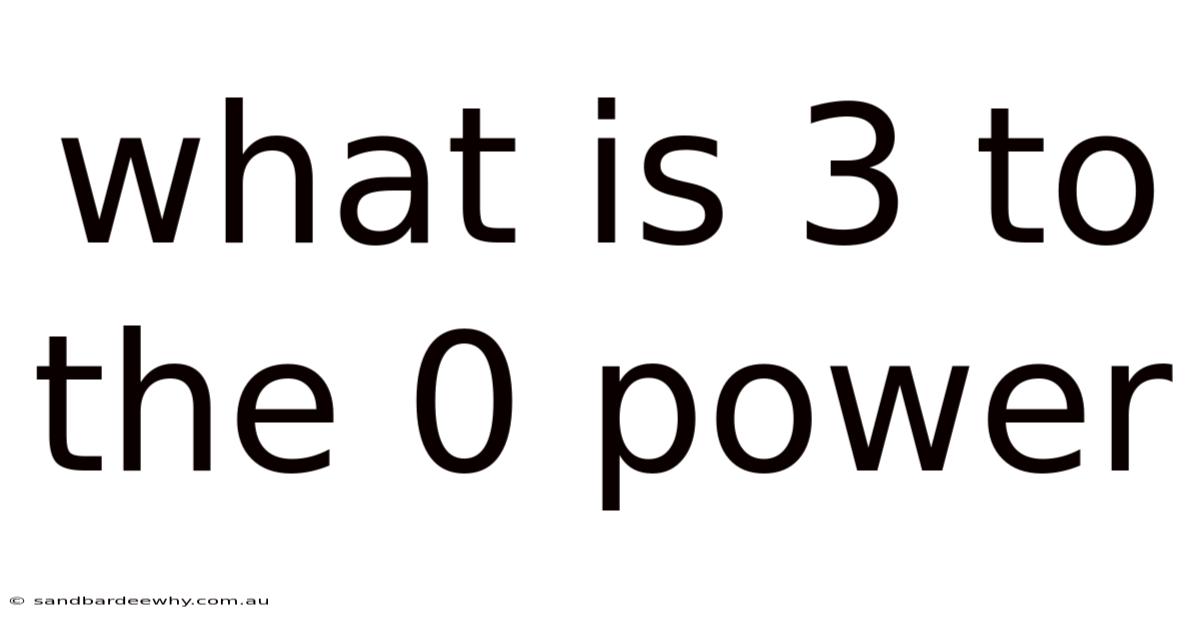
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where numbers dance in perfect harmony, each following a set of rules that govern their relationships. Among these rules, one of the most intriguing is the concept of raising a number to the power of zero. It might seem counterintuitive at first—how can you multiply a number by itself zero times? But when you unravel the mathematical principles behind it, you discover a profound elegance and consistency that underpins much of mathematics.
The concept of exponents is not merely an abstract mathematical idea; it is a fundamental tool used across various scientific and engineering disciplines. From calculating compound interest in finance to determining the rate of radioactive decay in physics, exponents provide a concise way to express repeated multiplication. Understanding what happens when an exponent is zero is crucial for maintaining the integrity and applicability of these calculations. Today, we'll explore the meaning of 3 to the 0 power, revealing why it equals 1 and illustrating its significance with real-world examples and expert insights.
Main Subheading
At first glance, raising a number to the power of zero might seem like a mathematical anomaly. After all, exponents typically denote repeated multiplication: (3^2) (3 squared) means 3 multiplied by itself, (3 \times 3), which equals 9. Similarly, (3^3) (3 cubed) means 3 multiplied by itself three times, (3 \times 3 \times 3), which equals 27. But what does it mean to multiply 3 by itself zero times? The intuitive answer might be zero, but that's not the case.
The real answer lies in the broader mathematical framework that exponents fit into. The rule that any non-zero number raised to the power of zero equals 1 is not arbitrary. It stems from the need for mathematical consistency and coherence across different operations and formulas. Understanding this rule requires a journey through the fundamental principles of exponents and their relationship to division. By establishing a clear understanding of these principles, we can appreciate why (3^0 = 1) and how this rule supports the logical structure of mathematics.
Comprehensive Overview
To understand why (3^0 = 1), we need to explore the properties of exponents and how they relate to division. Exponents are a shorthand way of expressing repeated multiplication. For any number a and positive integer n, (a^n) means multiplying a by itself n times.
The Division Rule of Exponents
One of the fundamental rules of exponents is the division rule, which states that when you divide two powers with the same base, you subtract the exponents:
[ \frac{a^m}{a^n} = a^{m-n} ]
This rule holds true as long as a is not zero. Let's consider an example with our base of 3:
[ \frac{3^3}{3^2} = \frac{3 \times 3 \times 3}{3 \times 3} = 3^{3-2} = 3^1 = 3 ]
Here, we see that dividing (3^3) by (3^2) simplifies to 3, which aligns with the rule of subtracting exponents.
Deriving the Zero-Exponent Rule
Now, let's extend this division rule to a scenario where the exponents are equal. Consider dividing (3^n) by itself:
[ \frac{3^n}{3^n} ]
According to the division rule of exponents, this simplifies to:
[ 3^{n-n} = 3^0 ]
However, any number divided by itself is equal to 1. Therefore:
[ \frac{3^n}{3^n} = 1 ]
Combining these two results, we have:
[ 3^0 = 1 ]
This derivation demonstrates that setting (3^0) to 1 is not an arbitrary choice but a logical consequence of the division rule of exponents. It ensures that the rules of exponents remain consistent and coherent.
Why Not Zero?
One might wonder, why can't (3^0) be zero? Suppose we defined (3^0 = 0). This would lead to contradictions in our mathematical system. Consider the division rule again:
[ \frac{3^n}{3^0} = 3^{n-0} = 3^n ]
If (3^0) were zero, then we would have:
[ \frac{3^n}{0} = 3^n ]
But division by zero is undefined in mathematics. Assigning zero to (3^0) would break the fundamental rules of arithmetic and render many mathematical operations inconsistent.
Mathematical Consistency
Defining (3^0 = 1) maintains consistency across various mathematical concepts and formulas. For instance, consider polynomial functions. A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables and coefficients, involving only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents.
For example, the polynomial (f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c) can be written more generally as:
[ f(x) = a_2x^2 + a_1x^1 + a_0x^0 ]
Here, (a_0) is a constant term. If (x^0) were not equal to 1, the constant term would disappear whenever (x) is non-zero, which would fundamentally alter the nature of polynomial functions. By defining (x^0 = 1), we ensure that the constant term remains constant regardless of the value of (x).
Generalization
The principle that any non-zero number raised to the power of zero equals 1 is a universal rule in mathematics. It applies to all real numbers (except zero itself, which is undefined) and even extends to complex numbers. This consistency is crucial for the seamless integration of different mathematical concepts and their applications in science and engineering.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the concept of (3^0 = 1) is a well-established mathematical principle, its implications and applications continue to evolve with advancements in various fields. In recent years, there has been increased emphasis on understanding the foundational principles of mathematics to enhance computational algorithms and models.
Computational Mathematics
In computational mathematics, the consistency of mathematical rules is paramount. Algorithms rely on predictable and coherent behavior to produce accurate results. The zero-exponent rule is integral to ensuring that these algorithms function correctly, especially in areas such as:
- Symbolic computation: Systems that manipulate mathematical expressions symbolically need to adhere to the zero-exponent rule to maintain accuracy.
- Numerical analysis: Approximating solutions to complex problems requires consistent application of mathematical principles, including the zero-exponent rule.
Educational Trends
Educationally, there is a growing trend towards emphasizing conceptual understanding over rote memorization. Instead of simply memorizing that (3^0 = 1), students are encouraged to understand the underlying mathematical principles that lead to this conclusion. This approach fosters a deeper appreciation for mathematics and improves problem-solving skills.
Public Perception
Popular math YouTubers and educational content creators often address common misconceptions about exponents and the zero-exponent rule. These platforms provide accessible explanations and visualizations that help demystify mathematical concepts for a broader audience. The emphasis is on showing why (3^0 = 1) rather than just stating it as a fact.
Philosophical Perspectives
From a philosophical perspective, the zero-exponent rule highlights the beauty and elegance of mathematical structures. It exemplifies how seemingly abstract concepts are interconnected and how consistency is a guiding principle in mathematical reasoning. This viewpoint encourages a deeper appreciation for the intrinsic harmony within mathematics.
Tips and Expert Advice
Understanding that (3^0 = 1) is more than just memorizing a rule; it's about grasping the underlying mathematical principles. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help solidify this concept:
Visualize Exponents
One effective way to understand exponents is to visualize them. Start with simple examples like (3^1 = 3), (3^2 = 9), and (3^3 = 27). Notice how each step involves multiplying by 3. Then, think about what happens when you "go backward" from (3^1) to (3^0). To maintain the pattern, you need to divide by 3, which leads to (3^0 = 3/3 = 1).
Use Real-World Examples
Relate exponents to real-world scenarios. For example, consider exponential growth or decay. The general formula for exponential growth is:
[ A = A_0(1 + r)^t ]
where:
- (A) is the final amount.
- (A_0) is the initial amount.
- (r) is the growth rate.
- (t) is the time period.
If (t = 0), then (A = A_0(1 + r)^0 = A_0 \times 1 = A_0), which means the final amount is equal to the initial amount when no time has passed. This makes intuitive sense and reinforces the idea that anything to the power of zero is 1.
Teach Others
One of the best ways to solidify your understanding of a concept is to teach it to someone else. Explain to a friend or family member why (3^0 = 1), using the division rule of exponents as your explanation. The process of explaining it will help you identify any gaps in your own understanding and reinforce your knowledge.
Practice Problems
Work through practice problems that involve exponents and the zero-exponent rule. This will help you apply the concept in different contexts and build confidence in your ability to use it correctly. For example, simplify expressions like:
[ \frac{5^4}{5^4} + 2^0 - 4^0 ]
By simplifying each term, you reinforce the concept:
[ 1 + 1 - 1 = 1 ]
Use Online Resources
Take advantage of online resources such as Khan Academy, Wolfram Alpha, and other educational websites. These platforms offer interactive lessons, videos, and practice problems that can help you deepen your understanding of exponents and the zero-exponent rule.
Understand the Limitations
Be aware of the limitations of the zero-exponent rule. It applies to all non-zero numbers. The expression (0^0) is undefined in mathematics because it leads to inconsistencies in different contexts. Understanding these limitations will help you avoid common mistakes and use the rule correctly.
FAQ
Q: Why does any non-zero number raised to the power of zero equal 1?
A: This is due to the division rule of exponents. When you divide a number raised to a power by itself, you subtract the exponents, resulting in the number raised to the power of zero. Since any number divided by itself is 1, it follows that any non-zero number raised to the power of zero must equal 1 to maintain mathematical consistency.
Q: What happens if you raise zero to the power of zero?
A: The expression (0^0) is generally considered undefined in mathematics. In some contexts, it might be defined as 1, but this can lead to inconsistencies in other areas, such as calculus and combinatorics. Therefore, it is best to consider (0^0) as undefined.
Q: Can the zero-exponent rule be applied to negative numbers?
A: Yes, the zero-exponent rule applies to all non-zero numbers, including negative numbers. For example, ((-3)^0 = 1). The base number can be positive or negative, as long as it is not zero.
Q: How does the zero-exponent rule relate to polynomial functions?
A: In polynomial functions, the zero-exponent rule ensures that the constant term remains constant regardless of the value of the variable. If (x^0) were not equal to 1, the constant term would disappear whenever (x) is non-zero, which would fundamentally alter the nature of polynomial functions.
Q: Is there a real-world application of the zero-exponent rule?
A: Yes, the zero-exponent rule is used in various real-world applications, particularly in exponential growth and decay models. It ensures that the initial amount remains unchanged when no time has passed, maintaining the consistency of the model.
Conclusion
In summary, the concept of (3^0 = 1) is a fundamental principle in mathematics rooted in the division rule of exponents and the need for mathematical consistency. Understanding why any non-zero number raised to the power of zero equals 1 is crucial for grasping the broader implications of exponents and their applications in various fields.
By visualizing exponents, relating them to real-world examples, teaching others, and practicing problems, you can solidify your understanding of this concept. Embrace the elegance and coherence of mathematics, and continue exploring the fascinating relationships between numbers and their properties.
To deepen your understanding, try working through additional exponent problems or exploring advanced mathematical concepts that build upon this foundation. Share this article with others who might find it helpful, and let's continue to unravel the mysteries of mathematics together.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Phrase Has The Most Negative Connotation
Nov 30, 2025
-
Summary Of The Great Gatsby Chapter 3
Nov 30, 2025
-
The Lungs Are Blank To The Heart
Nov 30, 2025
-
What Are The Two Types Of Pure Substances
Nov 30, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is 1 4 Lb
Nov 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 3 To The 0 Power . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.