What Is A 12 Out Of 30
sandbardeewhy
Nov 27, 2025 · 12 min read
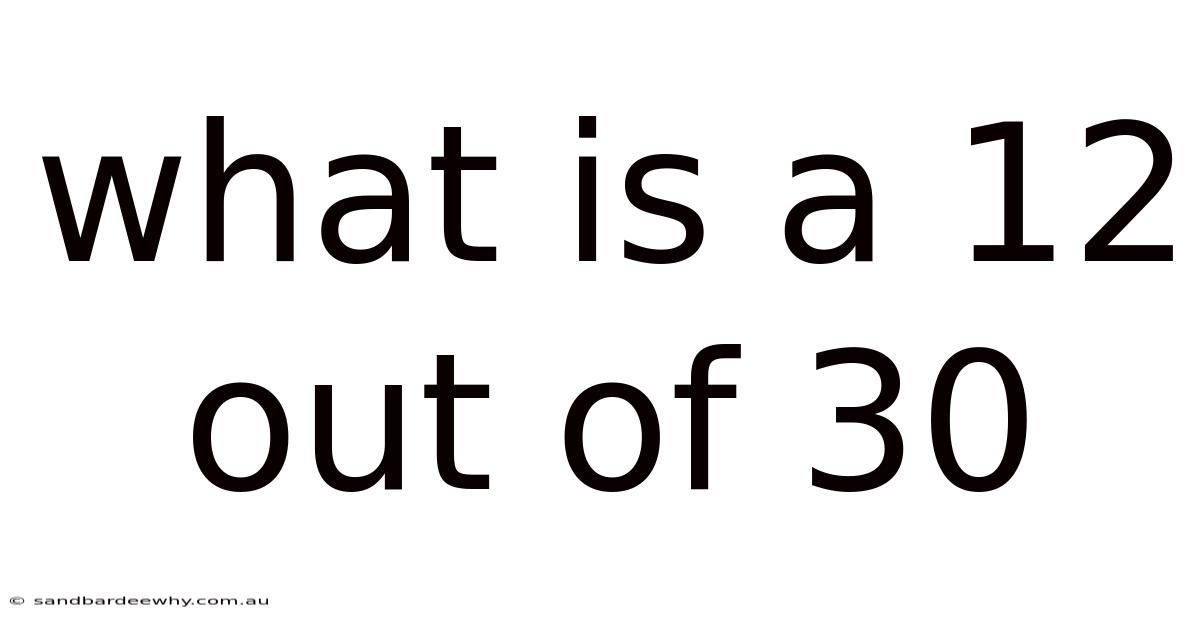
Table of Contents
Imagine you are a student anxiously awaiting the results of your latest math quiz. The teacher hands back the papers, and you see a large "12/30" scrawled at the top. A wave of mixed emotions washes over you: Is that good? Is it bad? What does it even mean in terms of my grade? This scenario is common, and understanding what a score like 12 out of 30 represents is crucial for students, parents, and educators alike. It's more than just a fraction; it's a window into your performance and areas for improvement.
Similarly, in professional settings, we often encounter metrics and scores presented as fractions. A project might be "8/10 complete," or a company might report "5/20" key performance indicators (KPIs) met. Understanding these figures quickly and accurately is essential for making informed decisions and tracking progress. Deconstructing a fraction like 12/30 involves understanding basic arithmetic, percentages, and how these concepts apply in various real-world scenarios.
Understanding the Score: 12 out of 30
At its most fundamental level, 12 out of 30 represents a fraction. The number 12, the numerator, indicates the number of points you earned or the number of successfully completed tasks. The number 30, the denominator, indicates the total possible points or the total number of tasks. Thus, in our initial example, you earned 12 points out of a possible 30 on your math quiz. This fraction provides a direct comparison of your achievement against the maximum possible.
Converting to Percentage
To gain a clearer understanding of the score, it's often helpful to convert the fraction into a percentage. Percentages provide a standardized way to compare scores and performance across different scales. The formula for converting a fraction to a percentage is simple:
(Numerator / Denominator) * 100 = Percentage
In our case, (12 / 30) * 100 = 40%
Therefore, a score of 12 out of 30 is equivalent to 40%. This means you achieved 40% of the total possible score. In many educational systems, 40% might be considered a failing grade or at least a score indicating significant room for improvement. However, the interpretation of this percentage depends heavily on the context, grading scale, and expectations.
Interpreting the Score in Different Contexts
The interpretation of a 40% score varies greatly depending on the context. In academics, a 40% on a test is generally considered low. Most grading scales in schools and universities consider 60% or higher as passing. Therefore, a 40% would likely result in a failing grade or a need for remediation.
However, in other fields, a 40% achievement might not be as discouraging. For instance, in sales, achieving 40% of your target in the first quarter of the year might be seen as a reasonable starting point, with opportunities for growth throughout the remaining quarters. Similarly, in project management, completing 40% of a complex project within a specific timeframe might be on track if the initial phases are the most challenging.
The Significance of Context
The significance of a 12/30 score, or its equivalent 40%, depends on several factors:
- Grading Scale: Different institutions and instructors use varying grading scales. Some may have a more lenient curve, while others might have stricter standards.
- Subject Difficulty: A 40% in an advanced calculus course might be viewed differently than a 40% in an introductory art class.
- Individual Performance: The student's prior performance and learning trajectory should be considered. A student who typically scores very low might see a 40% as an improvement.
- Purpose of Assessment: Is the assessment formative (designed to provide feedback and guide learning) or summative (designed to evaluate overall achievement)? A 40% on a formative assessment might be a valuable learning opportunity, while a 40% on a final exam might be more concerning.
Comprehensive Overview of Fractions, Percentages, and Performance Evaluation
To fully grasp the implications of a score like 12 out of 30, it's important to delve into the fundamentals of fractions, percentages, and how they're used in performance evaluation.
The Foundation of Fractions
A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of two main components: the numerator and the denominator. The denominator indicates the total number of equal parts into which the whole is divided, and the numerator indicates how many of those parts are being considered.
Fractions can be proper (numerator is less than the denominator, e.g., 1/2), improper (numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator, e.g., 3/2), or mixed (a whole number and a proper fraction, e.g., 1 1/2). Understanding the type of fraction can provide immediate insight. A proper fraction indicates a value less than one whole, while an improper fraction indicates a value of one whole or more.
Fractions can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD). For example, 12/30 can be simplified by dividing both by 6, resulting in 2/5. Simplifying fractions makes them easier to understand and compare.
The Power of Percentages
A percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100. The word "percent" comes from the Latin per centum, meaning "out of one hundred." Percentages are widely used because they provide a standardized way to express proportions and rates, making it easy to compare different quantities.
Converting a fraction to a percentage involves multiplying the fraction by 100, as we saw earlier. Percentages can also be converted back into fractions by dividing by 100. For example, 40% is equivalent to 40/100, which can be simplified to 2/5.
Percentages are used in a vast array of applications, from calculating discounts and interest rates to reporting economic indicators and survey results. Their universality makes them an essential tool for understanding and interpreting data.
Performance Evaluation Metrics
Performance evaluation is the systematic process of assessing an individual's or a group's performance against predetermined goals and standards. It's used in various settings, including education, business, sports, and the arts. Performance metrics provide a quantitative way to measure progress and identify areas for improvement.
Scores like 12 out of 30, or their percentage equivalents, are common performance metrics. However, it's crucial to interpret these metrics in conjunction with qualitative feedback. Numerical scores provide a snapshot of performance, while qualitative feedback offers context and insights into the why behind the numbers.
Effective performance evaluation systems incorporate both quantitative and qualitative data to provide a holistic view of performance. They also include mechanisms for feedback, coaching, and development to help individuals and teams improve their performance over time.
Common Misinterpretations and Pitfalls
Interpreting scores and percentages can be tricky, and it's essential to avoid common misinterpretations. One common pitfall is focusing solely on the numerical score without considering the context. As discussed earlier, the significance of a 40% depends heavily on the specific situation.
Another pitfall is comparing scores across different scales or assessments. A 40% on a highly challenging exam might be a better performance than a 70% on an easier one. Therefore, it's crucial to consider the difficulty level and grading criteria when comparing scores.
Additionally, it's important to avoid making generalizations based on a single score. Performance is dynamic and can fluctuate over time. A single low score should not be used to define an individual's abilities or potential. Instead, it should be viewed as an opportunity for learning and growth.
The Role of Feedback and Improvement
Regardless of the score, feedback is essential for learning and improvement. Feedback provides insights into strengths and weaknesses, helps individuals understand where they went wrong, and offers guidance on how to improve.
Effective feedback is specific, timely, and actionable. It should focus on behaviors and outcomes rather than personal attributes. It should also be delivered in a constructive and supportive manner, with the goal of helping the individual improve their performance.
In the case of a score like 12 out of 30, feedback should focus on the specific areas where the individual struggled. For example, if the score was on a math quiz, the feedback should identify the specific concepts or problem types that the student needs to work on. The feedback should also provide specific suggestions for improvement, such as reviewing specific chapters, practicing additional problems, or seeking help from a tutor.
Trends and Latest Developments in Performance Measurement
The field of performance measurement is constantly evolving, with new trends and developments emerging to improve accuracy, fairness, and effectiveness.
Holistic Assessment Approaches
There is a growing trend toward holistic assessment approaches that consider multiple aspects of performance. These approaches go beyond traditional numerical scores and incorporate qualitative data, such as peer reviews, self-assessments, and observations.
Holistic assessment provides a more comprehensive view of performance, capturing not only what an individual achieved but also how they achieved it. This approach is particularly valuable in fields where creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking are highly valued.
Adaptive Testing Technologies
Adaptive testing technologies are revolutionizing the way assessments are administered. These technologies adjust the difficulty level of questions based on the individual's performance, providing a more accurate measure of their abilities.
Adaptive testing can be more efficient and less stressful than traditional fixed-length tests. It also provides more detailed information about an individual's strengths and weaknesses, allowing for more targeted feedback and instruction.
Gamification and Engagement
Gamification techniques are increasingly being used to enhance engagement and motivation in performance measurement. By incorporating game-like elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, assessments can become more enjoyable and less intimidating.
Gamification can also provide valuable data on an individual's learning styles, preferences, and problem-solving strategies. This data can be used to personalize learning experiences and improve overall performance.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Data analytics and predictive modeling are being used to identify patterns and trends in performance data. These techniques can help organizations identify high-potential individuals, predict future performance, and develop targeted interventions to improve performance.
Data analytics can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of different assessment methods and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing large datasets, organizations can gain valuable insights into the factors that drive performance.
Tips and Expert Advice for Improving Performance
Improving performance requires a combination of effort, strategy, and effective feedback. Here are some tips and expert advice for enhancing performance in various settings:
Set Clear Goals
Clearly defined goals are essential for effective performance. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). When goals are clear, individuals know what they need to achieve and can track their progress.
For example, instead of setting a vague goal like "improve my grades," set a SMART goal like "increase my score on the next math quiz by 10% by reviewing the material for one hour each day."
Seek Feedback Regularly
Feedback is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and tracking progress. Don't wait for formal performance reviews to seek feedback. Ask for feedback from teachers, supervisors, peers, and mentors on a regular basis.
When seeking feedback, be specific about the areas you want feedback on. For example, instead of asking "How am I doing?" ask "What could I do to improve my problem-solving skills?"
Focus on Strengths
While it's important to address weaknesses, it's equally important to focus on strengths. Identify your strengths and find ways to leverage them in your work.
When you focus on your strengths, you're more likely to be engaged and motivated. You're also more likely to produce high-quality work.
Practice Deliberately
Practice is essential for developing skills and improving performance. However, not all practice is created equal. Deliberate practice involves focusing on specific areas for improvement, seeking feedback, and making adjustments based on that feedback.
Deliberate practice is more effective than mindless repetition. It requires effort, focus, and a willingness to learn from mistakes.
Manage Time Effectively
Time management is crucial for balancing competing priorities and achieving goals. Use time management techniques, such as prioritizing tasks, setting deadlines, and avoiding distractions, to make the most of your time.
Experiment with different time management methods to find what works best for you. Some popular techniques include the Pomodoro Technique, the Eisenhower Matrix, and time blocking.
FAQ About Performance Scores
Q: What does a score of 12 out of 30 mean in terms of letter grades?
A: The equivalent letter grade depends on the specific grading scale used. However, a 40% (12/30) is generally considered a failing grade or a "D" in many educational systems.
Q: How can I improve my score if I get a 12 out of 30?
A: The first step is to identify the specific areas where you struggled. Review the material, seek feedback from teachers or mentors, practice deliberately, and set clear goals for improvement.
Q: Is a 12 out of 30 always a bad score?
A: Not necessarily. The significance of the score depends on the context, the difficulty of the assessment, and your prior performance. It's important to consider all factors before drawing conclusions.
Q: What is the difference between formative and summative assessments?
A: Formative assessments are designed to provide feedback and guide learning, while summative assessments are designed to evaluate overall achievement. A 12/30 on a formative assessment is a valuable learning opportunity, while a 12/30 on a summative assessment might be more concerning.
Q: How can I convert a score like 12 out of 30 into a percentage?
A: Divide the numerator (12) by the denominator (30) and multiply by 100. In this case, (12 / 30) * 100 = 40%.
Conclusion
Understanding what a score like 12 out of 30 means involves more than just basic arithmetic. It requires an understanding of fractions, percentages, performance evaluation metrics, and the specific context in which the score is being used. A 12 out of 30, equivalent to 40%, typically indicates a need for improvement, but its true significance depends on various factors, including the grading scale, subject difficulty, and individual performance.
Remember, performance scores are just one piece of the puzzle. They should be used in conjunction with qualitative feedback and a focus on continuous learning and improvement. Whether you're a student striving for better grades or a professional seeking to enhance your performance, understanding and interpreting performance scores effectively is crucial for achieving your goals. Now that you understand what a score of 12 out of 30 represents, take the next step: analyze your performance, seek feedback, and create a plan for improvement. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and let's learn and grow together!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Two Types Of Interference
Nov 27, 2025
-
1 2 Mile How Many Yards
Nov 27, 2025
-
How Did Europe Change After Napoleon Was Defeated
Nov 27, 2025
-
What Is Role Conflict In Sociology
Nov 27, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is The Quadratic Parent Function
Nov 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A 12 Out Of 30 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.