What Is The Percent Of 1 9
sandbardeewhy
Nov 29, 2025 · 12 min read
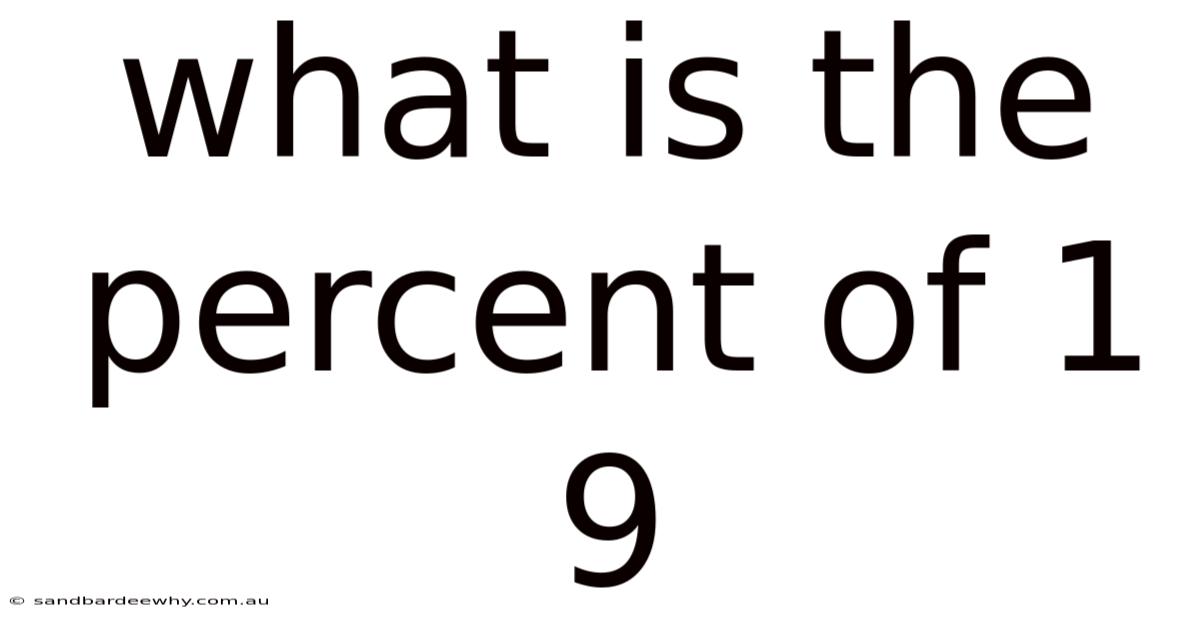
Table of Contents
Imagine you're at a lively farmer's market, and a vendor is selling ripe, juicy mangoes. He tells you, "One out of every nine mangoes in this batch is extra sweet!" You're immediately curious and want to know exactly what portion of the mangoes that represents. That's where the concept of "percent of 1 9" comes into play – it's the same as figuring out what percentage of the mangoes are extra sweet.
Understanding percentages is a fundamental skill that extends far beyond the farmer's market. From calculating discounts at your favorite store to analyzing statistical data at work, percentages are a ubiquitous tool for understanding proportions and making informed decisions. Let's delve into how we can precisely calculate what percent 1 is of 9 and explore the broader applications of percentage calculations in everyday life.
Main Subheading
The question "what is the percent of 1 9" is a basic mathematical problem involving the concept of percentages. Percentages are a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100. In simpler terms, a percentage tells you how many parts out of 100 a particular quantity represents. Understanding how to calculate percentages is essential in various fields, from finance and economics to science and everyday situations.
To find what percent 1 is of 9, we need to express 1 as a fraction of 9 and then convert that fraction into a percentage. The formula to do this is straightforward:
Percentage = (Part / Whole) * 100
In this case, 1 is the "part" and 9 is the "whole." So, the calculation would look like this:
Percentage = (1 / 9) * 100
This simple calculation opens the door to understanding proportional relationships, comparing different quantities, and making informed decisions based on numerical data. Before we dive into the calculation, let's explore the background and significance of percentages to better appreciate their importance.
Comprehensive Overview
The concept of percentages dates back to ancient Rome. As the Roman Empire expanded, the need for standardized taxation and financial calculation became crucial. The Romans often calculated taxes based on fractions of assets, such as centesima rerum venalium, which meant one-hundredth of the goods sold. This system was a precursor to the modern concept of percentages.
During the Middle Ages, as trade and commerce flourished in Europe, the use of percentages became more widespread. Italian merchants frequently used percentages to calculate interest rates, profits, and losses. The term "percent" itself is derived from the Italian per cento, meaning "out of one hundred." The adoption of Arabic numerals and the decimal system further facilitated the use of percentages in mathematical calculations.
The formalization of percentages as a mathematical tool occurred during the Renaissance and the Scientific Revolution. Mathematicians like Simon Stevin, who introduced decimal fractions to Europe, played a key role in standardizing the notation and application of percentages. By the 17th century, percentages were commonly used in various scientific, financial, and statistical analyses.
Mathematically, a percentage is a dimensionless number, meaning it does not have any units. It is simply a way of expressing a proportion or ratio. The symbol "%" is used to denote percentages. The basic formula to calculate a percentage is:
Percentage = (Part / Whole) * 100
This formula can be applied in various contexts. For example:
- Calculating a discount: If an item originally priced at $100 is on sale for $80, the discount is ($100 - $80) / $100 * 100 = 20%.
- Determining a grade: If a student scores 75 out of 100 on a test, their grade is (75 / 100) * 100 = 75%.
- Analyzing market share: If a company has 30 out of 100 customers in a market, their market share is (30 / 100) * 100 = 30%.
Understanding percentages also involves being able to convert between percentages, fractions, and decimals. Here are some examples:
- Percentage to Decimal: To convert a percentage to a decimal, divide by 100. For example, 25% = 25 / 100 = 0.25.
- Decimal to Percentage: To convert a decimal to a percentage, multiply by 100. For example, 0.75 = 0.75 * 100 = 75%.
- Percentage to Fraction: To convert a percentage to a fraction, divide by 100 and simplify. For example, 50% = 50 / 100 = 1/2.
- Fraction to Percentage: To convert a fraction to a percentage, multiply by 100. For example, 1/4 = (1/4) * 100 = 25%.
Percentages are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they are practical tools used daily in various aspects of life. In finance, percentages are used to calculate interest rates, investment returns, and loan payments. In statistics, they help analyze data, compare results, and make predictions. In retail, percentages are used for discounts, sales tax, and profit margins. Understanding and using percentages effectively can significantly enhance decision-making and problem-solving skills in both professional and personal contexts.
Trends and Latest Developments
Recent trends indicate an increasing reliance on data analysis and statistical methods across various industries, making percentage calculations more relevant than ever. Here’s a look at some key developments and how percentages play a crucial role:
-
E-commerce and Retail Analytics:
- E-commerce platforms use percentages extensively to track conversion rates (the percentage of website visitors who make a purchase), click-through rates (the percentage of users who click on a specific link), and customer retention rates (the percentage of customers who continue to purchase over a period).
- Retailers use percentage calculations to determine optimal pricing strategies, discount rates, and to analyze sales trends. For example, understanding the percentage increase in sales after a promotion helps in planning future marketing campaigns.
-
Financial Analysis:
- In finance, percentage change is a vital metric for assessing investment performance, economic growth, and inflation rates. Investors use percentage returns to evaluate the profitability of their portfolios.
- Financial analysts rely on percentage ratios (e.g., debt-to-equity ratio, profit margin) to assess the financial health and stability of companies.
-
Healthcare Statistics:
- Healthcare professionals use percentages to analyze patient outcomes, mortality rates, and the effectiveness of treatments. For instance, the percentage of patients recovering from a disease after a specific treatment provides valuable insights into its efficacy.
- Public health agencies use percentage data to track the prevalence of diseases, vaccination rates, and the success of public health initiatives.
-
Education and Assessment:
- Educators use percentages to grade assignments, calculate student averages, and assess overall academic performance. Standardized test scores are often reported as percentiles, indicating the percentage of students who scored below a particular level.
- Educational institutions also use percentage data to analyze admission rates, graduation rates, and student retention rates to improve educational programs and policies.
-
Environmental Science:
- Environmental scientists use percentages to monitor pollution levels, deforestation rates, and the impact of climate change. For example, the percentage increase in greenhouse gas emissions over a certain period is a critical indicator of environmental degradation.
- Conservation efforts often rely on percentage targets, such as increasing the percentage of protected areas or reducing the percentage of endangered species.
Popular opinion and statistical data increasingly highlight the importance of data literacy, which includes a strong understanding of percentage calculations. Data literacy is the ability to understand, interpret, and communicate data effectively. As data becomes more pervasive in our lives, being able to work with percentages is crucial for making informed decisions and critically evaluating information.
Professional insights reveal that while the basic formula for calculating percentages remains constant, the application and interpretation of percentage data are becoming more sophisticated. Here are some advanced considerations:
- Weighted Averages: In many real-world scenarios, data points have different levels of importance. Weighted averages, which involve multiplying each data point by its weight (expressed as a percentage), provide a more accurate representation of the overall trend. For example, calculating a student's final grade based on different assignment weights.
- Percentage Change vs. Percentage Point Change: It's important to distinguish between percentage change (the relative change between two values) and percentage point change (the absolute difference between two percentages). Confusing these two concepts can lead to misinterpretations.
- Simpson's Paradox: This statistical phenomenon occurs when trends appear in different groups of data but disappear or reverse when the groups are combined. Understanding Simpson's Paradox requires careful analysis of percentage data and awareness of potential confounding factors.
Tips and Expert Advice
Calculating percentages might seem straightforward, but mastering the skill requires understanding nuances and avoiding common pitfalls. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to enhance your proficiency with percentages:
-
Understand the Base Value:
- Tip: Always identify the "whole" or the base value against which the percentage is being calculated. Misidentifying the base value is a common error that leads to incorrect results.
- Example: If a store offers a 20% discount on an item originally priced at $50, the base value is $50. The discount amount is 20% of $50, which is $10. The sale price is $50 - $10 = $40.
-
Convert Percentages to Decimals and Fractions:
- Tip: Converting percentages to decimals or fractions can simplify calculations, especially when dealing with more complex problems.
- Example: To find 15% of 300, convert 15% to a decimal by dividing by 100 (15% = 0.15). Then, multiply 0.15 by 300 to get 45. Alternatively, convert 15% to a fraction (15% = 15/100 = 3/20) and multiply 3/20 by 300 to get 45.
-
Use Proportions:
- Tip: Set up proportions to solve for unknown values in percentage problems. Proportions can help you visualize the relationship between the part, the whole, and the percentage.
- Example: If you know that 30 is 25% of a number, you can set up the proportion: 30 / x = 25 / 100. Cross-multiplying gives 25x = 3000, so x = 120.
-
Calculate Percentage Change Accurately:
- Tip: Use the correct formula for percentage change: [( \frac{{\text{New Value - Old Value}}}{{\text{Old Value}}} \times 100 )] Ensure you use the original value as the denominator to find the correct relative change.
- Example: If a company's revenue increased from $200,000 to $250,000, the percentage increase is [( \frac{{250,000 - 200,000}}{{200,000}} \times 100 = 25% )]
-
Avoid Common Mistakes:
- Tip: Be cautious with percentage increases and decreases. A percentage increase followed by the same percentage decrease will not return you to the original value.
- Example: If an item's price increases by 10% from $100 to $110, and then decreases by 10%, the new price is 90% of $110, which is $99, not $100.
-
Use Technology to Verify:
- Tip: Utilize calculators, spreadsheet software (like Excel), or online percentage calculators to verify your manual calculations. Technology can help reduce errors and save time.
- Example: When dealing with complex financial calculations or large datasets, use Excel functions like
RATE,PV,FV, andPMTto calculate interest rates, present values, future values, and loan payments accurately.
-
Apply Percentages in Real-World Scenarios:
- Tip: Practice applying percentages in everyday situations, such as calculating discounts while shopping, determining tips at restaurants, or analyzing personal financial data.
- Example: When dining out, if your bill is $45 and you want to leave a 20% tip, calculate 20% of $45 (0.20 * 45 = $9). Add the tip to the bill for a total of $54.
-
Understand Weighted Percentages:
- Tip: When some data points are more important than others, use weighted percentages. Multiply each value by its weight (expressed as a percentage) before summing.
- Example: In a course, if homework is worth 30%, quizzes are worth 30%, and the final exam is worth 40%, and a student scores 80% on homework, 90% on quizzes, and 85% on the final exam, the weighted average is [( (0.30 \times 80) + (0.30 \times 90) + (0.40 \times 85) = 85% )]
By mastering these tips and practicing regularly, you can enhance your ability to work with percentages confidently and accurately in various contexts.
FAQ
Q: How do I calculate what percentage one number is of another?
A: To find what percentage a number (the "part") is of another number (the "whole"), divide the part by the whole and then multiply by 100. The formula is: Percentage = (Part / Whole) * 100.
Q: What is the difference between percentage increase and percentage decrease? A: Percentage increase is calculated as [( \frac{{\text{New Value - Old Value}}}{{\text{Old Value}}} \times 100 )] and indicates how much a quantity has grown. Percentage decrease is calculated similarly but indicates how much a quantity has shrunk.
Q: How do I convert a percentage to a decimal? A: To convert a percentage to a decimal, divide the percentage by 100. For example, 25% becomes 0.25.
Q: How do I convert a decimal to a percentage? A: To convert a decimal to a percentage, multiply the decimal by 100. For example, 0.75 becomes 75%.
Q: What is a percentage point? A: A percentage point is the simple difference between two percentages. For example, if a company's market share increased from 10% to 15%, that's a 5 percentage point increase.
Q: How can I calculate a discount using percentages? A: To calculate a discount, multiply the original price by the discount percentage (expressed as a decimal). Then, subtract the discount amount from the original price.
Q: What is a weighted average, and how is it calculated? A: A weighted average is an average where each value is multiplied by a weight. To calculate it, multiply each value by its weight (expressed as a percentage), and then sum the results.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding how to calculate "what is the percent of 1 9" is a fundamental skill with widespread applications. The calculation, (1 / 9) * 100, yields approximately 11.11%, illustrating that 1 is about 11.11% of 9. This concept extends beyond simple math problems, playing a crucial role in finance, statistics, retail, and everyday decision-making.
From calculating discounts and analyzing sales trends to interpreting financial data and assessing health outcomes, percentages are an essential tool for interpreting data and making informed decisions. By mastering the tips and techniques discussed, you can confidently apply percentages in real-world scenarios, enhancing your analytical and problem-solving skills.
Now that you have a solid understanding of percentage calculations, put your knowledge into practice. Calculate the percentage of your savings interest, analyze a recent sales promotion, or simply determine the tip amount at your next restaurant visit. Embrace the power of percentages to make informed decisions and gain deeper insights into the world around you.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Chapter 7 Summary For The Outsiders
Nov 29, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is Four Quarts
Nov 29, 2025
-
How Much Is 2 Quarts In Oz
Nov 29, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 10 Out Of 50
Nov 29, 2025
-
Words That Start With An E In Spanish
Nov 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Percent Of 1 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.