What Percent Is 16 Of 80
sandbardeewhy
Dec 04, 2025 · 10 min read
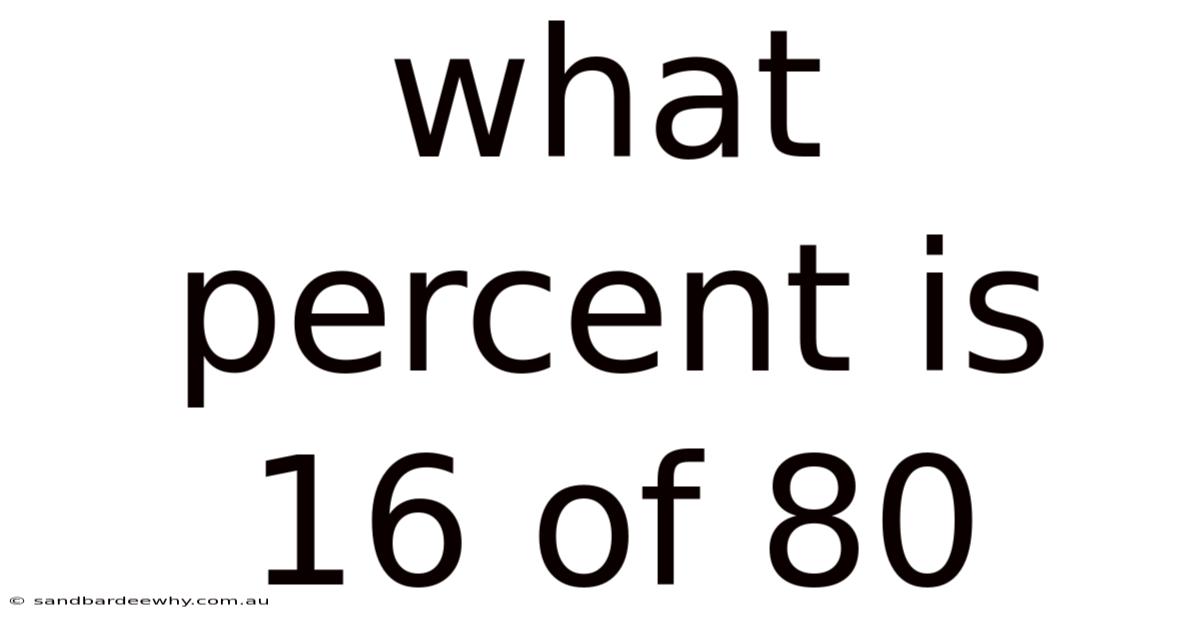
Table of Contents
Imagine you're at a bustling farmers market, eyeing a vibrant display of ripe, juicy apples. There are 80 apples in total, and you decide to buy 16 of them. The question that pops into your head is, "What percentage of the total apples am I taking?" This simple scenario highlights a fundamental mathematical concept: calculating percentages.
Percentage calculations aren't confined to farmers markets; they're woven into the fabric of our daily lives. From understanding discounts at your favorite store to figuring out the interest rate on a loan, grasping percentages is an essential skill. In this article, we'll dive deep into the straightforward calculation of determining what percent 16 is of 80, while also exploring the broader applications and nuances of percentage calculations in various contexts. Prepare to demystify percentages and empower yourself with a practical mathematical tool.
Main Subheading
Percentages are a ubiquitous part of modern life, appearing in everything from financial reports to nutritional information. Understanding how to calculate them is a fundamental skill that empowers individuals to make informed decisions. The question "What percent is 16 of 80?" is a simple yet illustrative example of percentage calculations.
At its core, a percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100. The term "percent" comes from the Latin per centum, meaning "out of one hundred." Thus, when we say "50 percent," we mean 50 out of every 100, or 50/100. This makes percentages incredibly useful for comparing proportions and understanding relative quantities.
Comprehensive Overview
To understand the concept of percentages more deeply, it's crucial to delve into their definition, scientific foundation, and historical context.
Definition of Percentage: A percentage is a dimensionless number, a ratio expressed as a fraction of 100. It provides a standardized way to represent proportions, making it easy to compare different quantities. The symbol "%" is used to denote percentage.
Scientific Foundation: The concept of percentage is rooted in basic mathematics, particularly in the areas of ratios and proportions. A percentage is essentially a ratio that has been scaled to have a denominator of 100. The formula to calculate a percentage is:
Percentage = (Part / Whole) × 100
In the case of "What percent is 16 of 80?", 16 is the part, and 80 is the whole. Applying the formula:
Percentage = (16 / 80) × 100
Percentage = 0.2 × 100
Percentage = 20%
Thus, 16 is 20% of 80.
History of Percentages: The use of percentages can be traced back to ancient Rome. As early as the Roman era, calculations involving fractions of 100 were used for assessing taxes, duties, and interest rates. However, the modern concept and notation of percentage became more formalized during the Renaissance. With the rise of commerce and banking, there was an increasing need for standardized ways to express financial quantities.
During the 15th century, merchants in Italy began using terms like "per cento" or "per cento" to calculate interest rates and profits. Over time, the term evolved into "percent." The percentage symbol "%" gradually developed from various abbreviations used in manuscripts. By the 17th century, the percentage notation was widely accepted and used in mathematical texts and commercial documents.
Essential Concepts Related to Percentages:
-
Base: The base is the total or whole quantity to which the percentage is applied. In our example, 80 is the base.
-
Rate: The rate is the percentage itself, expressed as a number out of 100. In our example, 20% is the rate.
-
Percentage: The percentage is the actual amount resulting from applying the rate to the base. In our example, 16 is the percentage.
-
Percentage Increase and Decrease: Percentage increase calculates how much a quantity has grown relative to its initial value. The formula is:
Percentage Increase = [(New Value - Initial Value) / Initial Value] × 100
Percentage decrease calculates how much a quantity has shrunk relative to its initial value. The formula is:
Percentage Decrease = [(Initial Value - New Value) / Initial Value] × 100
-
Percentage Change: This measures the relative change in a quantity, whether it's an increase or decrease. The formula is:
Percentage Change = [(New Value - Initial Value) / Initial Value] × 100
The absolute value of the result indicates the magnitude of the change, while the sign indicates whether it's an increase (positive) or decrease (negative).
Practical Applications: Percentages are used extensively across various domains:
- Finance: Calculating interest rates, investment returns, and profit margins.
- Retail: Determining discounts, sales tax, and markup percentages.
- Statistics: Expressing survey results, demographic data, and error margins.
- Science: Representing concentrations, errors in measurements, and changes in experimental data.
- Education: Grading exams, assessing performance, and comparing scores.
Trends and Latest Developments
In today's data-driven world, the use of percentages is more prevalent than ever. Various trends and developments highlight their importance and application in modern contexts:
Data Visualization: Percentages are widely used in data visualization to present information in an understandable format. Charts, graphs, and infographics often use percentages to represent proportions and distributions, making it easier for audiences to grasp complex data sets.
E-commerce and Marketing: Online retailers rely heavily on percentages to communicate discounts, promotions, and conversion rates. Understanding click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI) as percentages is crucial for optimizing marketing strategies and improving sales performance.
Financial Analysis: Financial analysts use percentages to assess company performance, analyze market trends, and evaluate investment opportunities. Key metrics such as profit margins, debt-to-equity ratios, and earnings growth are often expressed as percentages to provide a standardized basis for comparison.
Healthcare and Public Health: Percentages are used to track disease prevalence, vaccination rates, and other health indicators. Public health officials rely on percentage data to monitor trends, identify risk factors, and implement targeted interventions to improve population health outcomes.
Social Sciences: Researchers in the social sciences use percentages to analyze survey data, demographic trends, and social phenomena. Percentage data can reveal patterns and relationships, helping researchers draw meaningful conclusions and inform policy decisions.
Professional Insights: The accuracy and interpretation of percentage data are crucial. Misleading or poorly presented percentages can lead to misunderstandings and incorrect decisions. Therefore, it's essential to:
- Provide context: Always present percentages with relevant background information and context.
- Use appropriate denominators: Choose denominators that are meaningful and relevant to the analysis.
- Avoid small sample sizes: Be cautious when interpreting percentages based on small sample sizes, as they may not be representative of the larger population.
- Consider statistical significance: When comparing percentages, consider whether the differences are statistically significant or simply due to random variation.
Tips and Expert Advice
To master the use of percentages, here are some practical tips and expert advice:
1. Understand the Base: Always identify the base (the whole) to which the percentage is being applied. Misunderstanding the base can lead to incorrect calculations and misinterpretations. For example, if a store offers a 20% discount on an item, ensure you know whether the discount is applied before or after sales tax.
2. Convert Percentages to Decimals: To perform calculations, convert percentages to decimals by dividing by 100. For example, 20% becomes 0.20. This simplifies calculations and reduces the risk of errors.
3. Use Percentages to Compare Proportions: Percentages are excellent for comparing proportions between different groups or categories. However, be mindful of the sample sizes. A small percentage increase in a large population can represent a significant number of individuals, while a large percentage increase in a small group may not be as impactful.
4. Calculate Percentage Change Accurately: When calculating percentage change, use the correct formula:
Percentage Change = [(New Value - Initial Value) / Initial Value] × 100
Ensure you use the initial value as the denominator to accurately reflect the change relative to the starting point.
5. Apply Percentages in Real-World Scenarios: Practice applying percentages in everyday situations to reinforce your understanding. For example, calculate the tip amount at a restaurant, determine the sales tax on a purchase, or figure out the interest earned on a savings account.
6. Beware of Misleading Statistics: Be critical of how percentages are presented, especially in marketing materials and media reports. Look for potential biases, hidden agendas, and misleading comparisons. Always consider the source and the context of the data.
7. Use Technology to Your Advantage: Utilize calculators, spreadsheets, and online tools to perform percentage calculations quickly and accurately. These tools can save time and reduce the risk of errors, especially when dealing with complex calculations.
8. Understand Compound Interest: Compound interest is a powerful concept in finance where interest is earned not only on the principal but also on previously accumulated interest. Understanding how compound interest works can help you make informed decisions about investments and loans. The formula for compound interest is:
A = P (1 + r/n)^(nt)
Where:
* A = the future value of the investment/loan, including interest
* P = the principal investment amount (the initial deposit or loan amount)
* r = the annual interest rate (as a decimal)
* n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year
* t = the number of years the money is invested or borrowed for
9. Learn About Percentage Points: Percentage points are used to describe the difference between two percentages. For example, if a company's market share increases from 10% to 15%, the increase is 5 percentage points. This is different from a 50% increase (since 5 is 50% of 10).
10. Continuously Educate Yourself: Stay updated on the latest trends and developments in data analysis and statistics. Understanding how percentages are used in different contexts can help you make more informed decisions and communicate more effectively.
FAQ
Q: How do you convert a fraction to a percentage?
A: To convert a fraction to a percentage, divide the numerator by the denominator and multiply the result by 100. For example, to convert 3/4 to a percentage: (3 ÷ 4) × 100 = 75%.
Q: How do you calculate a percentage increase?
A: To calculate a percentage increase, use the formula: [(New Value - Initial Value) / Initial Value] × 100. For example, if a price increases from $20 to $25, the percentage increase is: [($25 - $20) / $20] × 100 = 25%.
Q: What is the difference between a percentage and a percentile?
A: A percentage is a ratio expressed as a fraction of 100, representing a proportion of a whole. A percentile, on the other hand, indicates the value below which a given percentage of observations in a group of observations falls. For example, if a student scores in the 90th percentile on a test, it means they scored higher than 90% of the other students.
Q: How can percentages be misleading?
A: Percentages can be misleading when they are presented without context, based on small sample sizes, or used to exaggerate small changes. Always consider the source of the data, the methodology used to calculate the percentages, and the potential for bias.
Q: What is a basis point?
A: A basis point is a unit of measure used in finance to describe the percentage change in the value or rate of a financial instrument. One basis point is equal to 0.01% (1/100 of a percent). Basis points are often used to express changes in interest rates, yields, and other financial metrics.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate percentages is a fundamental skill with broad applications across various domains. From finance and retail to healthcare and social sciences, percentages provide a standardized way to represent proportions, compare quantities, and analyze data. In this article, we've explored the concept of percentages, delving into their definition, scientific foundation, historical context, and practical applications. We've also examined current trends and developments in the use of percentages, along with expert tips and advice for mastering percentage calculations. By answering the question "What percent is 16 of 80?" and exploring related concepts, this article has provided a comprehensive guide to understanding and using percentages effectively.
Now that you have a solid grasp of percentages, take the next step and apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios. Whether you're calculating discounts, analyzing financial data, or interpreting survey results, put your skills to the test and empower yourself with the ability to make informed decisions. Share this article with others who may benefit from a better understanding of percentages and continue to explore the fascinating world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Mrs Who In A Wrinkle In Time
Dec 04, 2025
-
How Many Terms Can A Prime Minister Serve
Dec 04, 2025
-
How Do You Know How Many Protons An Element Has
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Is The Purpose Of A Map Scale
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Does The Upper Quartile Mean
Dec 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Percent Is 16 Of 80 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.