Z 1 X 2 Y 2
sandbardeewhy
Dec 05, 2025 · 10 min read
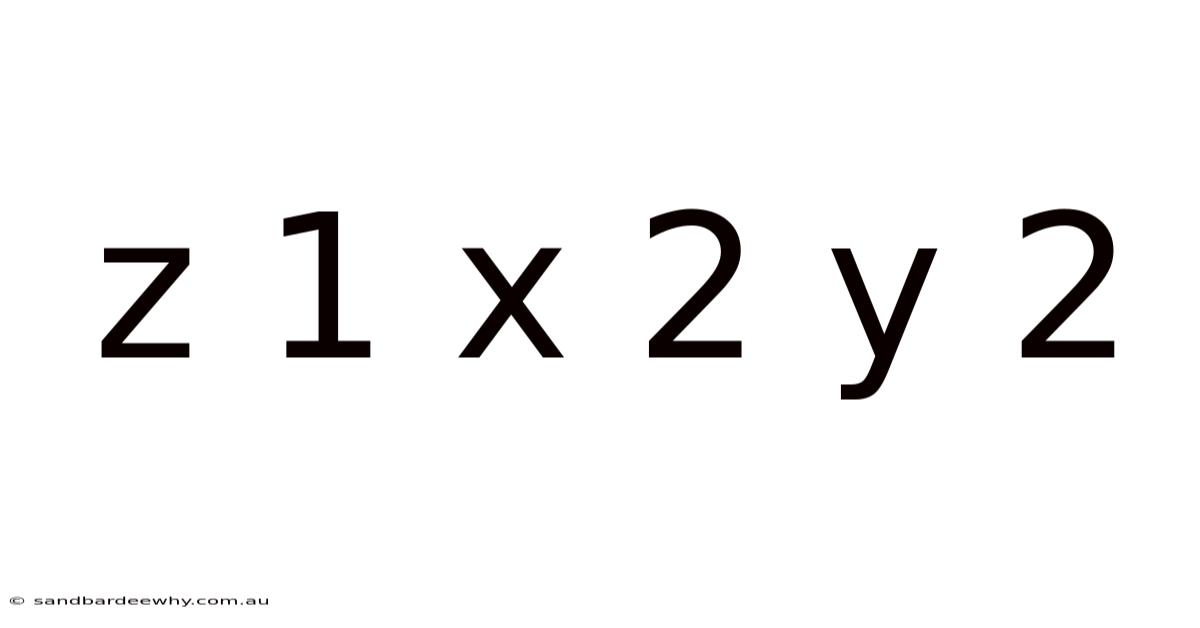
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where numbers dance and equations sing, where the seemingly abstract symbols of mathematics reveal hidden harmonies and profound truths. In this world, expressions like z 1 x 2 y 2 are not just a jumble of letters and digits, but rather keys to unlocking deeper understanding and powerful applications.
In the realm of mathematics, z 1 x 2 y 2 represents a fascinating expression with implications spanning various fields. It's a blend of variables and coefficients, a mathematical seed that can blossom into a multitude of interpretations and uses. Whether you're a student grappling with algebraic concepts, a seasoned engineer designing complex systems, or simply a curious mind eager to explore the language of the universe, understanding z 1 x 2 y 2 can open doors to new insights and possibilities.
The Essence of z 1 x 2 y 2: A Mathematical Exploration
The expression z 1 x 2 y 2 is fundamentally an algebraic term composed of variables (z, x, y) and coefficients (the numbers accompanying the variables). Let's break down each component to understand its role:
- Variables: In this context, z, x, and y are variables, meaning they represent unknown or changeable values. They act as placeholders that can be substituted with specific numbers to evaluate the expression.
- Coefficients: The numbers 1 and 2 are coefficients. A coefficient is a multiplicative factor that scales the variable it precedes. For instance, 2x means "two times the value of x." When a variable appears without an explicit coefficient, like z in z 1 x 2 y 2, it's understood that the coefficient is 1. So, z is the same as 1z.
- Exponents: The exponent of 2 associated with both x and y indicate that these variables are squared, meaning they are multiplied by themselves (x2 = x * x).
Therefore, z 1 x 2 y 2 can be interpreted as z multiplied by the square of x and the square of y. Mathematically, it's equivalent to:
z * x2 * y2 or z * (x * x) * (y * y)
The Foundation of Algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that uses symbols to represent numbers and quantities in formulas and equations. It provides a powerful framework for solving problems and expressing relationships between different elements. Understanding expressions like z 1 x 2 y 2 is a fundamental building block in algebra, enabling you to:
- Generalize relationships: Algebra allows you to express relationships between variables in a general way, rather than just with specific numbers.
- Solve equations: By manipulating algebraic expressions, you can solve equations to find the values of unknown variables.
- Model real-world phenomena: Many real-world situations can be modeled using algebraic equations, allowing you to analyze and predict outcomes.
Historical Roots
The development of algebra has a rich history spanning several civilizations. Ancient Babylonian mathematicians developed techniques for solving linear and quadratic equations. The ancient Greeks, particularly Diophantus, made significant contributions to the development of symbolic algebra. However, it was the Islamic scholars of the medieval period who truly advanced algebra, giving it its name (from the Arabic word al-jabr, meaning "reunion of broken parts") and developing systematic methods for solving equations. Al-Khwarizmi, a 9th-century Persian mathematician, is often considered the "father of algebra." Over the centuries, algebra continued to evolve, with contributions from mathematicians across Europe and the world, eventually leading to the sophisticated algebraic systems we use today.
The Power of Variables and Coefficients
Variables and coefficients are the heart and soul of algebra. They allow us to represent and manipulate quantities in a flexible and powerful way.
- Variables as placeholders: Variables act as placeholders for unknown or changing values. This allows us to write general equations that can be applied to a wide range of situations.
- Coefficients as scaling factors: Coefficients scale the variables, allowing us to adjust their impact on the overall expression. This is essential for modeling real-world phenomena where different factors have different weights.
Understanding Exponents
Exponents, like the "2" in x 2 and y 2, indicate the number of times a base is multiplied by itself. In the expression z 1 x 2 y 2, the exponents tell us that x and y are each multiplied by themselves. Understanding exponents is crucial for:
- Expressing repeated multiplication: Exponents provide a concise way to express repeated multiplication, such as x * x * x = x3.
- Describing growth and decay: Exponential functions are used to model growth and decay processes in various fields, such as finance, biology, and physics.
- Simplifying expressions: Exponent rules allow us to simplify complex expressions involving powers.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the core concepts of algebra remain timeless, their applications and the tools used to manipulate them are constantly evolving. Here are some current trends and developments related to expressions like z 1 x 2 y 2:
- Symbolic Computation Software: Software like Mathematica, Maple, and SageMath can perform complex algebraic manipulations, including simplifying expressions, solving equations, and plotting graphs. These tools are invaluable for researchers and engineers who work with complex mathematical models.
- Machine Learning and Symbolic Regression: Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being used to discover mathematical relationships from data. Symbolic regression, in particular, aims to find algebraic expressions that fit a given dataset. This can be used to identify underlying physical laws or create predictive models.
- Algebraic Geometry and Cryptography: Algebraic geometry, which studies the geometric properties of algebraic equations, plays a crucial role in modern cryptography. Elliptic curve cryptography, for example, relies on the properties of elliptic curves defined by algebraic equations.
- Quantum Computing and Linear Algebra: Quantum computing relies heavily on linear algebra, which is a generalization of algebra that deals with vectors and matrices. Quantum algorithms often involve manipulating complex algebraic expressions in high-dimensional spaces.
- Data Analysis and Modeling: Algebraic expressions are used extensively in data analysis and modeling to represent relationships between variables, create predictive models, and understand complex systems. Software packages like R and Python provide powerful tools for performing algebraic computations and data visualization.
These developments highlight the enduring importance of algebra and its ability to adapt to new challenges and opportunities in various fields. The ability to understand and manipulate algebraic expressions like z 1 x 2 y 2 remains a critical skill for anyone working in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
Tips and Expert Advice
Mastering algebraic expressions like z 1 x 2 y 2 requires practice and a strategic approach. Here are some tips and expert advice to help you succeed:
-
Build a Strong Foundation: Ensure you have a solid understanding of basic algebraic concepts, such as variables, coefficients, exponents, and order of operations. Without a strong foundation, it will be difficult to tackle more complex problems. Review fundamental concepts and practice basic exercises until you feel confident.
-
Practice Regularly: Like any skill, algebra requires consistent practice. Work through a variety of problems, starting with simple ones and gradually increasing the difficulty. The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with manipulating algebraic expressions.
-
Break Down Complex Problems: When faced with a complex problem, break it down into smaller, more manageable steps. Identify the key variables, coefficients, and exponents, and then use algebraic rules to simplify the expression. This will make the problem less daunting and easier to solve.
-
Use Visual Aids: Visual aids, such as graphs and diagrams, can be helpful for understanding algebraic concepts. For example, you can graph the equation y = x 2 to visualize the relationship between x and y. Visualizing the problem can often lead to new insights and solutions.
-
Check Your Work: Always check your work to ensure that you have not made any mistakes. Substitute your solution back into the original equation to see if it holds true. If you find an error, go back and review your steps to identify the mistake.
-
Understand the Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): Always follow the correct order of operations (Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) when simplifying algebraic expressions. This will ensure that you arrive at the correct answer. For example, in the expression 2 + 3 * 4, you must perform the multiplication before the addition.
-
Master Factoring: Factoring is the process of breaking down an algebraic expression into its constituent factors. This is a powerful technique for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and identifying common factors. Practice factoring different types of expressions, such as quadratic equations and differences of squares.
-
Learn to Recognize Patterns: Many algebraic problems involve recognizing patterns. For example, the difference of squares pattern (a 2 - b 2 = (a + b)(a - b)) can be used to quickly factor certain types of expressions. By learning to recognize patterns, you can solve problems more efficiently.
-
Use Technology Wisely: While it's important to develop your algebraic skills manually, technology can be a valuable tool for checking your work and exploring complex concepts. Use symbolic computation software like Mathematica or Maple to verify your solutions and experiment with different algebraic expressions.
-
Seek Help When Needed: Don't be afraid to ask for help when you're struggling with an algebraic problem. Talk to your teacher, a tutor, or a classmate. Explaining the problem to someone else can often help you clarify your own understanding and identify the source of your confusion.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between a variable and a constant?
A: A variable is a symbol that represents an unknown or changeable value, while a constant is a fixed value that does not change. For example, in the expression 2x + 3, x is a variable and 2 and 3 are constants.
Q: How do I simplify algebraic expressions?
A: To simplify algebraic expressions, you can use a variety of techniques, such as combining like terms, factoring, and applying the order of operations. The goal is to rewrite the expression in a simpler form without changing its value.
Q: What is the purpose of solving equations?
A: The purpose of solving equations is to find the values of the unknown variables that make the equation true. This can be used to solve real-world problems, such as determining the optimal price for a product or predicting the trajectory of a projectile.
Q: How do I factor a quadratic equation?
A: To factor a quadratic equation of the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0, you need to find two numbers that multiply to ac and add up to b. Once you find those numbers, you can rewrite the equation as (x + r)(x + s) = 0, where r and s are the two numbers you found.
Q: What is the relationship between algebra and calculus?
A: Algebra is a foundation for calculus. Calculus builds upon algebraic concepts to study rates of change and accumulation. Many of the techniques used in calculus, such as differentiation and integration, rely on algebraic manipulation.
Conclusion
The expression z 1 x 2 y 2, seemingly simple, embodies fundamental algebraic principles with wide-ranging applications. From understanding the roles of variables and coefficients to appreciating the power of exponents, mastering these concepts opens doors to solving complex problems and modeling real-world phenomena. As technology advances, the ability to manipulate algebraic expressions becomes increasingly vital for success in STEM fields.
Now that you've explored the depths of z 1 x 2 y 2, consider taking the next step in your mathematical journey. Practice simplifying similar expressions, explore more advanced algebraic concepts, and consider using symbolic computation software to deepen your understanding. Share this article with fellow learners and engage in discussions about the fascinating world of algebra!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Z 1 X 2 Y 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.