Is A Negative Minus A Negative A Positive
sandbardeewhy
Nov 30, 2025 · 10 min read
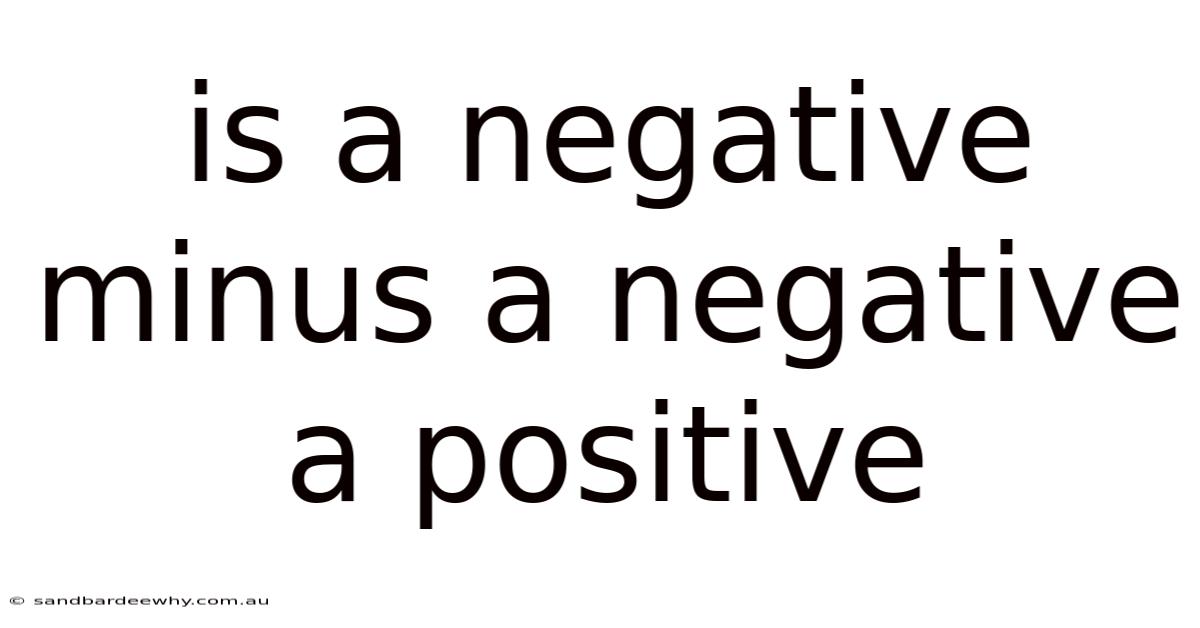
Table of Contents
Imagine yourself walking into a bakery, ready to buy some delicious treats. The baker tells you that you owe him $5, but then realizes he actually owes you $5. This cancels out your debt and puts you $5 in the clear. In the world of mathematics, this is essentially what happens when you subtract a negative number: it turns into addition, transforming what seems like a loss into a gain.
We often hear the phrase "a negative minus a negative is a positive," but understanding why this is true can sometimes be a challenge. It's not just a mathematical rule to memorize; it's a concept rooted in the very nature of numbers and how they interact. Grasping this principle is fundamental to building a solid foundation in mathematics, opening doors to more complex concepts and problem-solving techniques. This article will dive deep into the logic behind this seemingly simple statement, exploring its theoretical underpinnings, practical applications, and real-world examples.
Main Subheading
At first glance, the statement "a negative minus a negative is a positive" can appear counterintuitive. Many people learn it as a rote rule without understanding the deeper logic. To truly grasp this concept, it's important to move beyond memorization and explore the underlying principles of numbers and operations.
Understanding this principle requires a journey into the heart of mathematical thinking. The idea that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding its positive counterpart has significant implications for various mathematical fields, including algebra, calculus, and even physics. It's a concept that appears frequently, often without explicit recognition, and it underpins many of the calculations and manipulations we perform in these areas. Whether you're a student struggling with basic arithmetic or someone looking to refresh your understanding of fundamental mathematical principles, this exploration will provide clarity and insight.
Comprehensive Overview
Let's begin with a fundamental definition: a negative number is a real number that is less than zero. It represents the opposite of a positive number. For example, if 5 represents five steps forward, then -5 represents five steps backward. This concept of direction is crucial in understanding how negative numbers interact with subtraction.
Subtraction, at its core, is the operation of finding the difference between two numbers. It can be thought of as "taking away" one quantity from another. When we subtract a positive number, we move to the left on the number line. For instance, 5 - 3 means starting at 5 and moving 3 units to the left, resulting in 2. But what happens when we subtract a negative number?
To understand why subtracting a negative number becomes addition, let's consider the concept of additive inverses. The additive inverse of a number is the value that, when added to the original number, results in zero. For example, the additive inverse of 5 is -5, because 5 + (-5) = 0. Similarly, the additive inverse of -3 is 3, because -3 + 3 = 0. Subtraction can be redefined as adding the additive inverse. That is, a - b is the same as a + (-b).
Now, let's apply this to the case of subtracting a negative number. Suppose we have the expression 5 - (-3). According to our redefinition of subtraction, this is equivalent to 5 + (-(-3)). The term -(-3) represents the additive inverse of -3. We already know that the additive inverse of -3 is 3. Therefore, 5 - (-3) is the same as 5 + 3, which equals 8. In essence, subtracting a negative number is the same as adding its positive counterpart. This is why a negative minus a negative becomes a positive.
Historically, the understanding and acceptance of negative numbers took time. Ancient mathematicians initially struggled with the concept of quantities less than zero. It wasn't until the development of algebra and the formalization of number systems that negative numbers became widely accepted and used. Mathematicians like Brahmagupta in India, during the 7th century, were among the first to treat negative numbers as legitimate mathematical entities, recognizing their properties and developing rules for operations involving them. The formal rules for manipulating negative numbers, including the principle that subtracting a negative is equivalent to adding a positive, became more firmly established during the European Renaissance as algebraic notation became more standardized.
This principle isn't just an abstract rule; it has deep connections to various areas of mathematics and physics. In algebra, it's fundamental to simplifying expressions and solving equations. In calculus, it appears when dealing with derivatives and integrals. In physics, it's essential for working with vectors and forces, where direction is crucial. For example, consider a force acting in the opposite direction (negative). If you subtract that force, you are effectively adding a force in the positive direction.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the basic principle of "a negative minus a negative is a positive" remains constant, the way it's taught and applied continues to evolve. Modern educational approaches emphasize conceptual understanding over rote memorization. Teachers use visual aids, real-world examples, and interactive simulations to help students grasp the logic behind the rule.
One popular approach involves the use of number lines. By visually representing numbers and operations on a line, students can see how subtracting a negative number results in a movement to the right, which is equivalent to addition. Another trend is the use of manipulatives, such as colored chips or counters, where different colors represent positive and negative values. By physically manipulating these objects, students can develop a more intuitive understanding of how negative numbers interact with subtraction.
In advanced mathematics and physics, the concept extends to more complex domains. In linear algebra, subtracting a negative vector is equivalent to adding a vector in the opposite direction. In quantum mechanics, dealing with negative energy states requires a deep understanding of how negative numbers operate within complex mathematical frameworks. These advanced applications underscore the enduring importance of understanding the fundamental principle that subtracting a negative is the same as adding a positive.
Furthermore, current pedagogical research emphasizes the importance of addressing common misconceptions about negative numbers. Many students struggle with the idea that negative numbers can represent actual quantities or that they have the same "reality" as positive numbers. Addressing these misconceptions through targeted instruction and real-world examples is crucial for building a strong foundation in mathematics.
Tips and Expert Advice
1. Visualize the Number Line: One of the most effective ways to understand subtracting a negative number is to visualize it on a number line. Draw a number line and mark the starting point. When subtracting a positive number, move to the left. When subtracting a negative number, move to the right. This simple visualization can make the concept much clearer. For example, to calculate 3 - (-2), start at 3 on the number line. Since you are subtracting -2, move 2 units to the right. This lands you at 5, so 3 - (-2) = 5.
2. Use Real-World Examples: Abstract mathematical concepts can be difficult to grasp without concrete examples. Try relating negative numbers and subtraction to real-world situations. For example, think about temperature. If the temperature is -5 degrees Celsius and then increases by 3 degrees (subtracting a negative), the new temperature is -2 degrees Celsius. Similarly, consider debt. If you owe someone $10 (-$10) and they forgive $5 of your debt (subtracting a negative), you now owe $5 (-$5). These examples can help make the concept more relatable and understandable.
3. Break It Down into Steps: If you're struggling with a problem involving subtracting a negative number, break it down into smaller steps. First, identify the negative number being subtracted. Then, remember that subtracting a negative is the same as adding its positive counterpart. Rewrite the problem using addition instead of subtraction. Finally, perform the addition. For example, consider the expression -4 - (-6). First, identify that -6 is being subtracted. Then, rewrite the expression as -4 + 6. Finally, perform the addition: -4 + 6 = 2.
4. Practice Regularly: Like any mathematical skill, understanding subtracting negative numbers requires regular practice. Work through a variety of problems involving different negative numbers and operations. Start with simple examples and gradually increase the complexity. Use online resources, textbooks, or worksheets to find practice problems. The more you practice, the more confident and proficient you will become.
5. Understand the Additive Inverse: The concept of the additive inverse is crucial for understanding why subtracting a negative number is the same as adding its positive counterpart. Remember that the additive inverse of a number is the value that, when added to the original number, results in zero. For example, the additive inverse of -7 is 7, and the additive inverse of 4 is -4. Subtraction can be redefined as adding the additive inverse. So, a - b is the same as a + (-b). This understanding can help you see why subtracting a negative number becomes addition: a - (-b) = a + b.
6. Use Manipulatives: Manipulatives, such as colored chips or counters, can be a useful tool for visualizing negative numbers and operations. Assign one color to represent positive values and another color to represent negative values. For example, use red chips for negative values and blue chips for positive values. Then, physically manipulate the chips to represent subtraction and addition. For example, to calculate 3 - (-2), start with three blue chips (positive 3). To subtract -2, you need to take away two red chips. Since there are no red chips to take away, add two red chips and two blue chips (which is equivalent to adding zero). Now you can take away the two red chips, leaving you with five blue chips (positive 5).
FAQ
Q: Why does subtracting a negative number turn into addition?
A: Subtracting a negative number is equivalent to adding its positive counterpart because subtraction can be redefined as adding the additive inverse. The additive inverse of a number is the value that, when added to the original number, results in zero. So, subtracting a negative number is the same as adding its additive inverse, which is a positive number.
Q: Can you provide a simple example?
A: Sure! Consider the expression 5 - (-2). This is the same as 5 + 2, which equals 7. Subtracting -2 is the same as adding 2.
Q: Is this rule always true?
A: Yes, this rule is always true for real numbers. It's a fundamental principle of arithmetic and algebra.
Q: How does this apply to algebra?
A: In algebra, this rule is essential for simplifying expressions and solving equations. For example, if you have the equation x - (-3) = 7, you can simplify it to x + 3 = 7 and then solve for x.
Q: Are there any common mistakes to avoid?
A: Yes, one common mistake is forgetting to change the sign when subtracting a negative number. Always remember that subtracting a negative is the same as adding a positive. Another mistake is confusing subtraction with multiplication. The rule only applies to subtraction, not multiplication.
Conclusion
Understanding why "a negative minus a negative is a positive" is more than just memorizing a rule. It's about grasping the fundamental principles of numbers and operations. By understanding the concept of additive inverses and visualizing operations on a number line, you can gain a deeper appreciation for this seemingly simple statement. This understanding is crucial for building a solid foundation in mathematics and for tackling more complex problems in algebra, calculus, and beyond.
Now that you've explored the logic and applications of this principle, put your knowledge to the test! Try working through some practice problems and see if you can explain the concept to someone else. The best way to solidify your understanding is to actively engage with the material. Share this article with friends or classmates who might also benefit from a clearer understanding of this fundamental mathematical concept. Happy calculating!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 3 To The 0 Power
Nov 30, 2025
-
What Is Omniscient Third Person Point Of View
Nov 30, 2025
-
14 Out Of 25 As A Percentage
Nov 30, 2025
-
Chapter 3 Summary Of Lord Of The Flies
Nov 30, 2025
-
Major Rivers In Appalachian Plateau Georgia
Nov 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is A Negative Minus A Negative A Positive . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.